| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Visualize the addition of a chromosome that leads to Down syndrome in this video simulation .
An individual with more than the correct number of chromosome sets (two for diploid species) is called polyploid . For instance, fertilization of an abnormal diploid egg with a normal haploid sperm would yield a triploid zygote. Polyploid animals are extremely rare, with only a few examples among the flatworms, crustaceans, amphibians, fish, and lizards. Polyploid animals are sterile because meiosis cannot proceed normally and instead produces mostly aneuploid daughter cells that cannot yield viable zygotes. Rarely, polyploid animals can reproduce asexually by haplodiploidy, in which an unfertilized egg divides mitotically to produce offspring. In contrast, polyploidy is very common in the plant kingdom, and polyploid plants tend to be larger and more robust than euploids of their species ( [link] ).

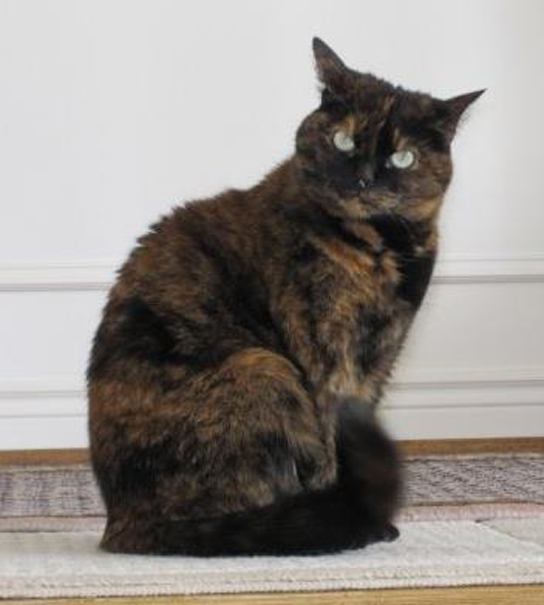
Humans display dramatic deleterious effects with autosomal trisomies and monosomies. Therefore, it may seem counterintuitive that human females and males can function normally, despite carrying different numbers of the X chromosome. Rather than a gain or loss of autosomes, variations in the number of sex chromosomes are associated with relatively mild effects. In part, this occurs because of a molecular process called X inactivation . Early in development, when female mammalian embryos consist of just a few thousand cells (relative to trillions in the newborn), one X chromosome in each cell inactivates by tightly condensing into a quiescent (dormant) structure called a Barr body. The chance that an X chromosome (maternally or paternally derived) is inactivated in each cell is random, but once the inactivation occurs, all cells derived from that one will have the same inactive X chromosome or Barr body. By this process, females compensate for their double genetic dose of X chromosome. In so-called “tortoiseshell” cats, embryonic X inactivation is observed as color variegation ( [link] ). Females that are heterozygous for an X-linked coat color gene will express one of two different coat colors over different regions of their body, corresponding to whichever X chromosome is inactivated in the embryonic cell progenitor of that region.

An individual carrying an abnormal number of X chromosomes will inactivate all but one X chromosome in each of her cells. However, even inactivated X chromosomes continue to express a few genes, and X chromosomes must reactivate for the proper maturation of female ovaries. As a result, X-chromosomal abnormalities are typically associated with mild mental and physical defects, as well as sterility. If the X chromosome is absent altogether, the individual will not develop in utero.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology 9-11 grades' conversation and receive update notifications?