| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The Enabling Grids for E-sciencE (EGEE) project provides an e-Research platform to the European research community and their international collaborators for high throughput data analysis for over 17,000 users across 160 projects. With a heritage stretching back over nearly a decade, EGEE-III (and its proceeding projects EGEE-II, EGEE-I and the European Data Grid) is a 32M € project funded by the European Commission to implement and deploy a distributed computing infrastructure to support researchers in many scientific domains, such as astrophysics, biomedicine, computational chemistry, earth sciences, high energy physics, finance, fusion, geophysics and multimedia. In addition, there are several applications from business sectors running on the EGEE Grid, such as applications from geophysics and the plastics industry. This chapter introduces the EGEE project in detail, considering middleware, security issues, access to information, data, compute resources, deployment and application development. It concludes with a look at sustainability.
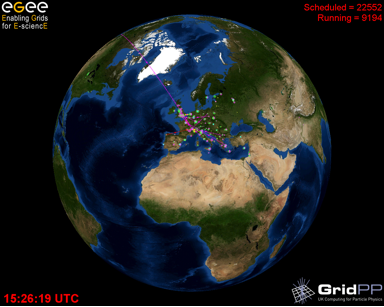
Grids are characterised by decentralised access to shared resources. These resources consist of computers, disks, and the network connections that link them together. Seamless, secure and scalable access to these resources, which may be owned by different organisations and could encompass different operating systems and architectures, is provided through software called middleware . Organisations that wish to cooperatively share their resources with their collaborators can do so without central control.
The gLite middleware distribution produced by the EGEE project is composed primarily of open-source software from many sources – some developed within the project and others from external providers. This software is integrated into a single software distribution before being tested and made available to sites for installation.
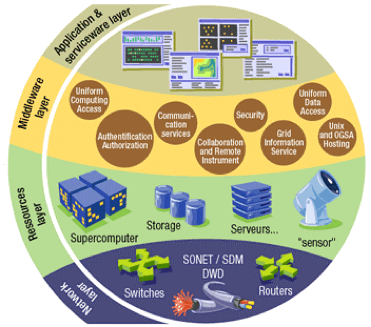
The software services used within gLite are there to enable researchers, through their own applications, to access the physical resources (disks, computers, instruments) that are attached to the EGEE infrastructure. These services have defined interfaces which allow developers to build their own applications.
The resources that make up the EGEE infrastructure are extremely valuable and access to these resources needs to be strictly controlled. Access to resources within EGEE is restricted to members of research collaborations (commonly called Virtual Organisations). Some resources may only allow individuals from a single Virtual Organisation to access their resources, while other resource providers will provide a shared resource to multiple Virtual Organisations spanning several research communities.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Research in a connected world' conversation and receive update notifications?