| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A cell is the smallest unit of a living thing. A living thing, like you, is called an organism. Thus, cells are the basic building blocks of all organisms.
In multicellular organisms, several cells of one particular kind interconnect with each other and perform shared functions to form tissues (for example, muscle tissue, connective tissue, and nervous tissue), several tissues combine to form an organ (for example, stomach, heart, or brain), and several organs make up an organ system (such as the digestive system, circulatory system, or nervous system). Several systems functioning together form an organism (such as an elephant, for example).
There are many types of cells, and all are grouped into one of two broad categories: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Animal cells, plant cells, fungal cells, and protist cells are classified as eukaryotic, whereas bacteria and archaea cells are classified as prokaryotic. Before discussing the criteria for determining whether a cell is prokaryotic or eukaryotic, let us first examine how biologists study cells.
Cells vary in size. With few exceptions, individual cells are too small to be seen with the naked eye, so scientists use microscopes to study them. A microscope is an instrument that magnifies an object. Most images of cells are taken with a microscope and are called micrographs.
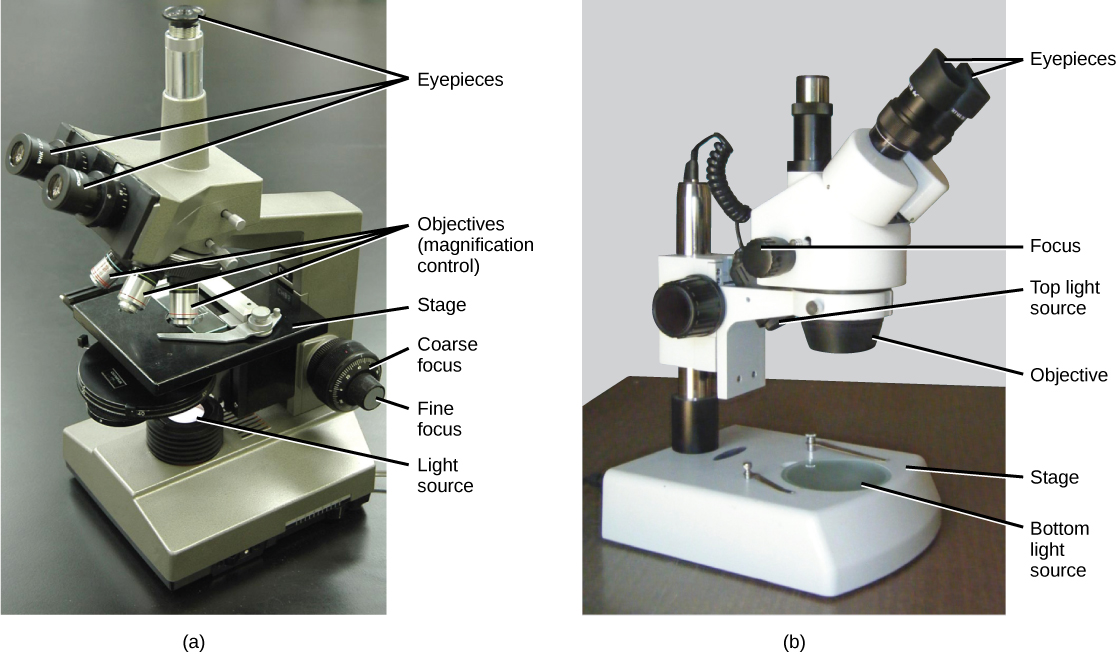
Light microscopes commonly used in the undergraduate college laboratory magnify up to approximately 400 times. Two parameters that are important in microscopy are magnification and resolving power. Magnification is the degree of enlargement of an object. Resolving power is the ability of a microscope to allow the eye to distinguish two adjacent structures as separate; the higher the resolution, the closer those two objects can be, and the better the clarity and detail of the image. When oil immersion lenses are used, magnification is usually increased to 1,000 times for the study of smaller cells, like most prokaryotic cells.
For another perspective on cell size, try the HowBig interactive.
A second type of microscope used in laboratories is the dissecting microscope ( [link] b ). These microscopes have a lower magnification (20 to 80 times the object size) than light microscopes and can provide a three-dimensional view of the specimen. Thick objects can be examined with many components in focus at the same time.
By the late 1830s, botanist Matthias Schleiden and zoologist Theodor Schwann were studying tissues and proposed the unified cell theory , which states that all living things are composed of one or more cells, that the cell is the basic unit of life, and that all new cells arise from existing cells. These principles still stand today.
A cell is the smallest unit of life. Most cells are so small that they cannot be viewed with the naked eye. Therefore, scientists must use microscopes to study cells. Electron microscopes provide higher magnification, higher resolution, and more detail than light microscopes. The unified cell theory states that all organisms are composed of one or more cells, the cell is the basic unit of life, and new cells arise from existing cells.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Environmental biology' conversation and receive update notifications?