| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Economic events can change the equilibrium salary (or wage) and quantity of labor. Consider how the wave of new information technologies, like computer and telecommunications networks, has affected low-skill and high-skill workers in the U.S. economy. From the perspective of employers who demand labor, these new technologies are often a substitute for low-skill laborers like file clerks who used to keep file cabinets full of paper records of transactions. However, the same new technologies are a complement to high-skill workers like managers, who benefit from the technological advances by being able to monitor more information, communicate more easily, and juggle a wider array of responsibilities. So, how will the new technologies affect the wages of high-skill and low-skill workers? For this question, the four-step process of analyzing how shifts in supply or demand affect a market (introduced in Demand and Supply ) works in this way:
Step 1. What did the markets for low-skill labor and high-skill labor look like before the arrival of the new technologies? In [link] (a) and [link] (b), S 0 is the original supply curve for labor and D 0 is the original demand curve for labor in each market. In each graph, the original point of equilibrium, E 0 , occurs at the price W 0 and the quantity Q 0 .
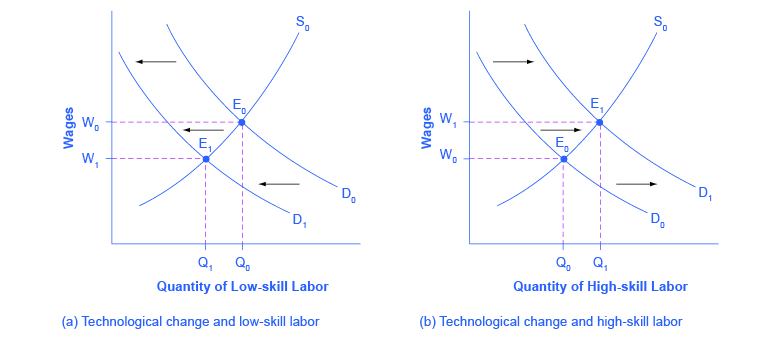
Step 2. Does the new technology affect the supply of labor from households or the demand for labor from firms? The technology change described here affects demand for labor by firms that hire workers.
Step 3. Will the new technology increase or decrease demand? Based on the description earlier, as the substitute for low-skill labor becomes available, demand for low-skill labor will shift to the left, from D 0 to D 1 . As the technology complement for high-skill labor becomes cheaper, demand for high-skill labor will shift to the right, from D 0 to D 1 .
Step 4. The new equilibrium for low-skill labor, shown as point E 1 with price W 1 and quantity Q 1 , has a lower wage and quantity hired than the original equilibrium, E 0 . The new equilibrium for high-skill labor, shown as point E 1 with price W 1 and quantity Q 1 , has a higher wage and quantity hired than the original equilibrium (E 0 ).
So, the demand and supply model predicts that the new computer and communications technologies will raise the pay of high-skill workers but reduce the pay of low-skill workers. Indeed, from the 1970s to the mid-2000s, the wage gap widened between high-skill and low-skill labor. According to the National Center for Education Statistics, in 1980, for example, a college graduate earned about 30% more than a high school graduate with comparable job experience, but by 2008, a college graduate earned about 70% more than an otherwise comparable high school graduate. Many economists believe that the trend toward greater wage inequality across the U.S. economy was primarily caused by the new technologies.
Visit this website to read about ten tech skills that have lost relevance in today’s workforce.
In the labor market, households are on the supply side of the market and firms are on the demand side. In the market for financial capital, households and firms can be on either side of the market: they are suppliers of financial capital when they save or make financial investments, and demanders of financial capital when they borrow or receive financial investments.
In the demand and supply analysis of labor markets, the price can be measured by the annual salary or hourly wage received. The quantity of labor can be measured in various ways, like number of workers or the number of hours worked.
Factors that can shift the demand curve for labor include: a change in the quantity demanded of the product that the labor produces; a change in the production process that uses more or less labor; and a change in government policy that affects the quantity of labor that firms wish to hire at a given wage. Demand can also increase or decrease (shift) in response to: workers’ level of education and training, technology, the number of companies, and availability and price of other inputs.
The main factors that can shift the supply curve for labor are: how desirable a job appears to workers relative to the alternatives, government policy that either restricts or encourages the quantity of workers trained for the job, the number of workers in the economy, and required education.
Identify each of the following as involving either demand or supply. Draw a circular flow diagram and label the flows A through F. (Some choices can be on both sides of the goods market.)
Predict how each of the following events will raise or lower the equilibrium wage and quantity of coal miners in West Virginia. In each case, sketch a demand and supply diagram to illustrate your answer.
National Center for Educational Statistics. “Digest of Education Statistics.” (2008 and 2010). Accessed December 11, 2013. nces.ed.gov.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Openstax microeconomics in ten weeks' conversation and receive update notifications?