| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Waxes are made up of a hydrocarbon chain with an alcohol (–OH) group and a fatty acid. Examples of animal waxes include beeswax and lanolin. Plants also have waxes, such as the coating on their leaves, that helps prevent them from drying out.
For an additional perspective on lipids, explore “Biomolecules: The Lipids” through this interactive animation .
Proteins are one of the most abundant organic molecules in living systems and have the most diverse range of functions of all macromolecules. Proteins may be structural, regulatory, contractile, or protective; they may serve in transport, storage, or membranes; or they may be toxins or enzymes. Each cell in a living system may contain thousands of different proteins, each with a unique function. Their structures, like their functions, vary greatly. They are all, however, polymers of amino acids, arranged in a linear sequence.
The functions of proteins are very diverse because there are 20 different chemically distinct amino acids that form long chains, and the amino acids can be in any order. For example, proteins can function as enzymes or hormones. Enzymes , which are produced by living cells, are catalysts in biochemical reactions (like digestion) and are usually proteins. Each enzyme is specific for the substrate (a reactant that binds to an enzyme) upon which it acts. Enzymes can function to break molecular bonds, to rearrange bonds, or to form new bonds. An example of an enzyme is salivary amylase, which breaks down amylose, a component of starch.
Hormones are chemical signaling molecules, usually proteins or steroids, secreted by an endocrine gland or group of endocrine cells that act to control or regulate specific physiological processes, including growth, development, metabolism, and reproduction. For example, insulin is a protein hormone that maintains blood glucose levels.
Proteins have different shapes and molecular weights; some proteins are globular in shape whereas others are fibrous in nature. For example, hemoglobin is a globular protein, but collagen, found in our skin, is a fibrous protein. Protein shape is critical to its function. Changes in temperature, pH, and exposure to chemicals may lead to permanent changes in the shape of the protein, leading to a loss of function or denaturation (to be discussed in more detail later). All proteins are made up of different arrangements of the same 20 kinds of amino acids.
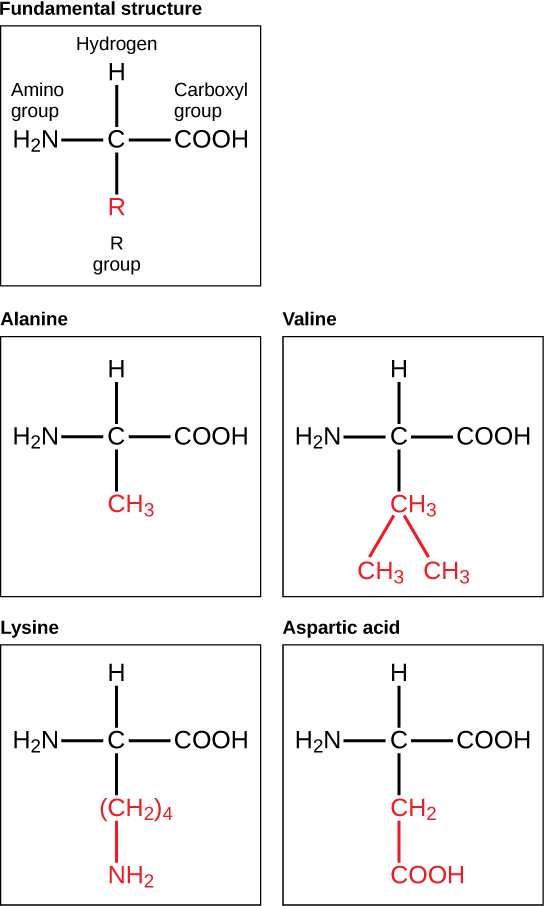
Amino acids are the monomers that make up proteins. Each amino acid has the same fundamental structure, which consists of a central carbon atom bonded to an amino group (–NH 2 ), a carboxyl group (–COOH), and a hydrogen atom. Every amino acid also has another variable atom or group of atoms bonded to the central carbon atom known as the R group. The R group is the only difference in structure between the 20 amino acids; otherwise, the amino acids are identical ( [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Environmental biology' conversation and receive update notifications?