| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
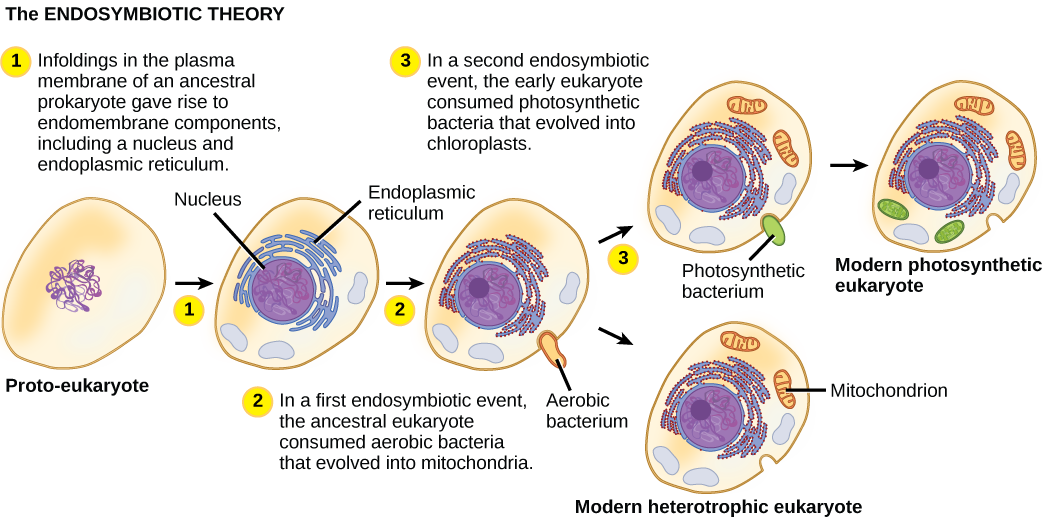
Mitochondria that carry out aerobic respiration have their own genomes, with genes similar to bacteria. However, many of the genes for proteins that are required in aerobic respiration are located in the nucleus. Additionally, in some eukaryotic groups, such genes are found in the mitochondria, whereas in other groups, they are found in the nucleus. This has been interpreted as evidence that genes have been transferred from the endosymbiont chromosome to the host genome. This loss of genes by the endosymbiont is probably one explanation why mitochondria cannot live without a host.
Some groups of eukaryotes are photosynthetic. Their cells contain, in addition to the standard eukaryotic organelles, another kind of organelle called a plastid . When such cells are carrying out photosynthesis, their plastids are rich in the pigment chlorophyll a and a range of other pigments, called accessory pigments, which are involved in harvesting energy from light. Photosynthetic plastids are called chloroplasts ( [link] ).
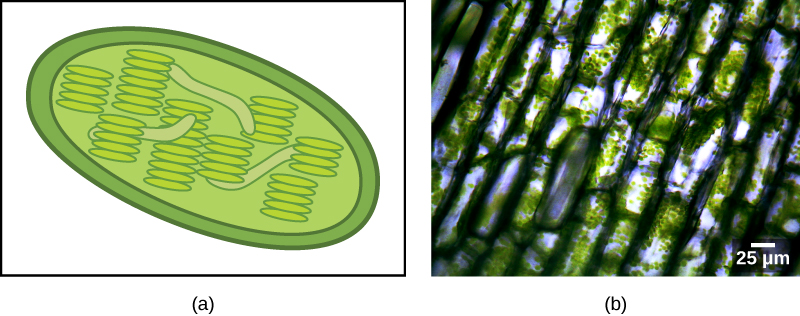
Like mitochondria, plastids appear to have an endosymbiotic origin. This hypothesis was also championed by Lynn Margulis. Plastids are derived from cyanobacteria that lived inside the cells of an ancestral, aerobic, heterotrophic eukaryote. This is called primary endosymbiosis, and plastids of primary origin are surrounded by two membranes.
There is also, as with the case of mitochondria, strong evidence that many of the genes of the endosymbiont were transferred to the nucleus. Plastids, like mitochondria, cannot live independently outside the host. In addition, like mitochondria, plastids are derived from the division of other plastids and never built from scratch. Researchers have suggested that the endosymbiotic event that led to Archaeplastida occurred 1 to 1.5 billion years ago, at least 5 hundred million years after the fossil record suggests that eukaryotes were present.
What evidence is there that mitochondria were incorporated into the ancestral eukaryotic cell before chloroplasts?
The oldest fossil evidence of eukaryotes is about 2 billion years old. Fossils older than this all appear to be prokaryotes. It is probable that today’s eukaryotes are descended from an ancestor that had a prokaryotic organization. The last common ancestor of today’s Eukarya had several characteristics, including cells with nuclei that divided mitotically and contained linear chromosomes where the DNA was associated with histones, a cytoskeleton and endomembrane system, and the ability to make cilia/flagella during at least part of its life cycle. It was aerobic because it had mitochondria that were the result of an aerobic alpha-proteobacterium that lived inside a host cell. Whether this host had a nucleus at the time of the initial symbiosis remains unknown. The last common ancestor may have had a cell wall for at least part of its life cycle, but more data are needed to confirm this hypothesis. Today’s eukaryotes are very diverse in their shapes, organization, life cycles, and number of cells per individual.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Bi 101 for lbcc ilearn campus' conversation and receive update notifications?