| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
ACTIVITY 1
To solve simple problems by forming and solving equations
[LO 2.2, 2.4]
How do we solve this problem?
Jamie’s dad is four times as old as Jamie. His father is 40. How old is Jamie?
a) We could think really hard, and try a few guesses. For instance: If Jamie is 1 year old, then his father must be 4. Not correct. What about 2 years old? And so on.
b) Make a table: Complete the empty spaces. Does this help?
| Age | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ||
| Age x 4 | 4 | 8 | 12 | 28 | 40 |
c) Draw a flow diagram: Is this useful?
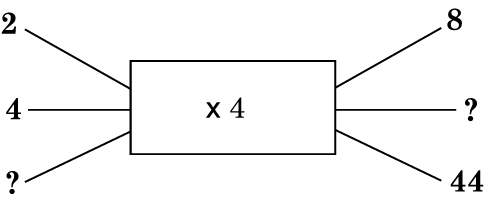
Jamie’s dad is four times as old as Jamie. If his father is 40, how old is Jamie?
A problem for you to do: Leon has 48 marbles. Amy has only a third as many as Leon; how many does she have? Use the last method.
The way you should set out your answer is:
State what the variable represents.
Please note that the first and last steps are in ordinary words, and the middle step(s) in algebra.
E x ercise:
Find the answers to the following problems:
1. Mr Jacobs has R295,45 in his pocket. Mrs Jacobs has R55,30 less than her husband in her purse. How much money does she have in her purse?
2. I think of a number. I multiply it by 7 and divide the answer by three. I get 49. What was the number I first thought of? Remember to check your answer.
3. In America Joanie buys an item that is marked $5,75. She works out that it would be R41,69 when she converts the dollars to rand. What is the rand/dollar exchange rate she used?
ACTIVITY 2
To develop effective methods for solving more complicated equations
[LO 2.3, 2.4]

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Mathematics grade 9' conversation and receive update notifications?