| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Kinetic energy is the energy an object has due to its motion.
Kinetic energy is the energy an object has because of its motion. This means that any moving object has kinetic energy. The faster it moves, the more kinetic energy it has. Kinetic energy ( ) is therefore dependent on the velocity of the object. The mass of the object also plays a role. A truck of , moving at , will have more kinetic energy than a car of , also moving at . Kinetic energy is defined as:
Consider the suitcase on the cupboard that was discussed earlier. When the suitcase falls, it will gain velocity (fall faster), until it reaches the ground with a maximum velocity. The suitcase will not have any kinetic energy when it is on top of the cupboard because it is not moving. Once it starts to fall it will gain kinetic energy, because it gains velocity. Its kinetic energy will increase until it is a maximum when the suitcase reaches the ground.
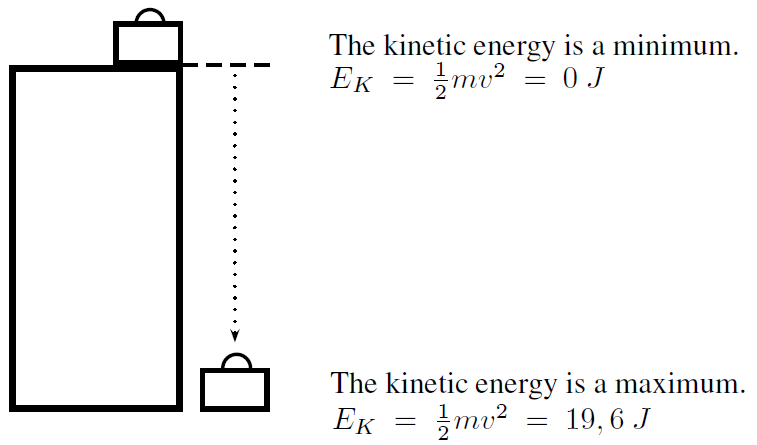
A brick falls off a high roof. It reaches the ground with a velocity of . What is the kinetic energy of the brick when it starts to fall and when it reaches the ground?
These are both in the correct units so we do not have to worry about unit conversions.
We are asked to find the kinetic energy of the brick at the top and the bottom. From the definition we know that to work out , we need to know the mass and the velocity of the object and we are given both of these values.
Since the brick is not moving at the top, its kinetic energy is zero.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physics - grade 10 [caps 2011]' conversation and receive update notifications?