| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
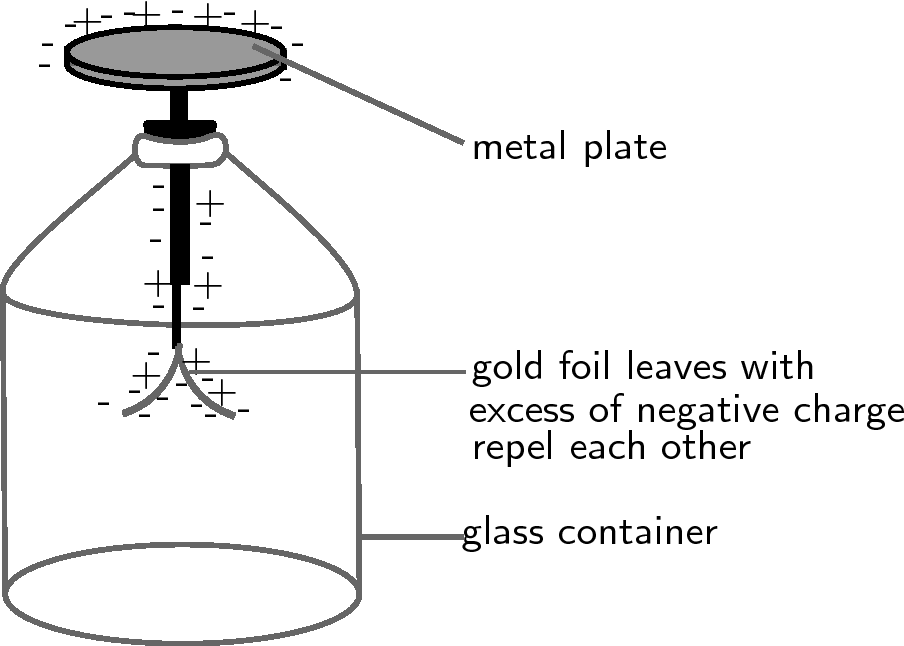
If you were to bring the charged rod close to the uncharged electroscope, and then you touched the metal plate with your finger at the same time, this would cause charge to flow up from the ground (the earth), through your body onto the metal plate. Connecting to the earth so charge flows is called grounding . The charge flowing onto the plate is opposite to the charge on the rod, since it is attracted to the charge on the rod. Therefore, for our picture, the charge flowing onto the plate would be negative. Now that charge has been added to the electroscope, it is no longer neutral, but has an excess of negative charge. Now if we move the rod away, the leaves will remain apart because they have an excess of negative charge and they repel each other. If we ground the electroscope again (this time without the charged rod nearby), the excess charge will flow back into the earth, leaving it neutral.
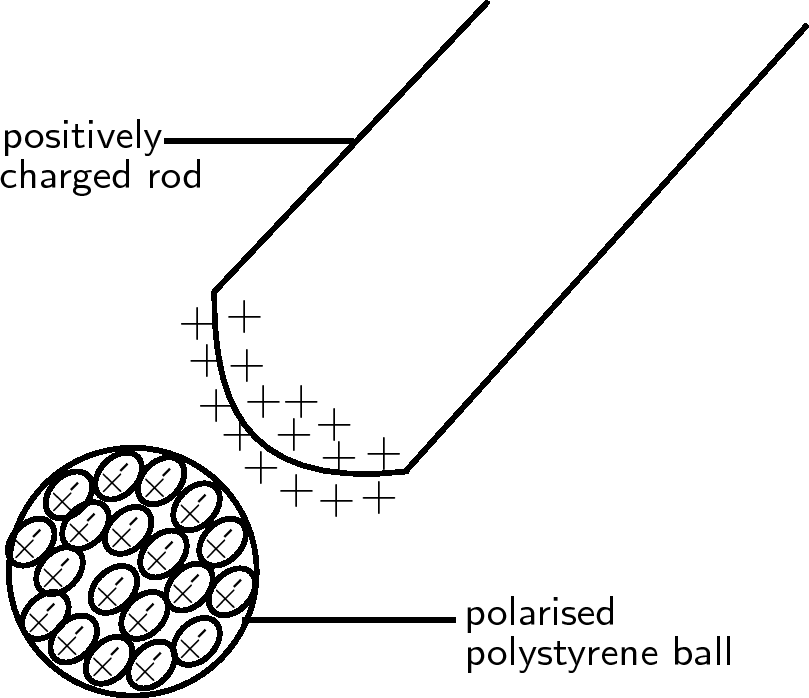
Unlike conductors, the electrons in insulators (non-conductors) are bound to the atoms of the insulator and cannot move around freely through the material. However, a charged object can stillexert a force on a neutral insulator due to a phenomenon called polarisation .
If a positively charged rod is brought close to a neutral insulator such as polystyrene, it can attract the bound electronsto move round to the side of the atoms which is closest to the rod and cause the positive nuclei to move slightlyto the opposite side of the atoms. This process is called polarisation . Although it is a very small (microscopic) effect, if there are many atoms and the polarised object islight (e.g. a small polystyrene ball), it can add up to enough force to cause the object to be attracted onto the charged rod. Remember, that the polystyreneis only polarised, not charged. The polystyrene ball is still neutral since no charge was added or removed from it. The picture showsa not-to-scale view of the polarised atoms in the polystyrene ball:
Some materials are made up of molecules which are already polarised. These are molecules which havea more positive and a more negative side but are still neutral overall. Just as a polarised polystyrene ball can be attracted to a charged rod, these materialsare also affected if brought close to a charged object.
Water is an example of a substance which is made of polarised molecules. If a positively charged rod is brought close to a stream of water, the molecules can rotateso that the negative sides all line up towards the rod. The stream of water will then be attracted to the rod since opposite charges attract.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physics - grade 10 [caps 2011]' conversation and receive update notifications?