| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Given and find the missing side and angles. If there is more than one possible solution, show both.
Solution 1
Solution 2
In the triangle shown in [link] , solve for the unknown side and angles. Round your answers to the nearest tenth.
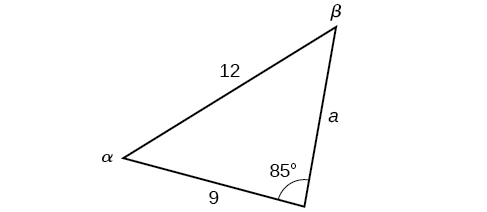
In choosing the pair of ratios from the Law of Sines to use, look at the information given. In this case, we know the angle and its corresponding side and we know side We will use this proportion to solve for
To find apply the inverse sine function. The inverse sine will produce a single result, but keep in mind that there may be two values for It is important to verify the result, as there may be two viable solutions, only one solution (the usual case), or no solutions.
In this case, if we subtract from 180°, we find that there may be a second possible solution. Thus, To check the solution, subtract both angles, 131.7° and 85°, from 180°. This gives
which is impossible, and so
To find the remaining missing values, we calculate Now, only side is needed. Use the Law of Sines to solve for by one of the proportions.
The complete set of solutions for the given triangle is
Given find the missing side and angles. If there is more than one possible solution, show both. Round your answers to the nearest tenth.
Find all possible triangles if one side has length 4 opposite an angle of 50°, and a second side has length 10.
Using the given information, we can solve for the angle opposite the side of length 10. See [link] .
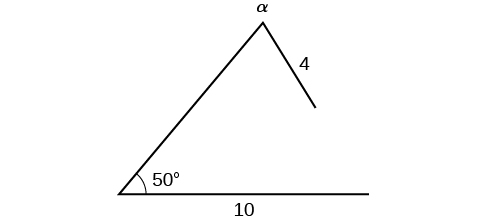
We can stop here without finding the value of Because the range of the sine function is it is impossible for the sine value to be 1.915. In fact, inputting in a graphing calculator generates an ERROR DOMAIN. Therefore, no triangles can be drawn with the provided dimensions.
Determine the number of triangles possible given
two
Now that we can solve a triangle for missing values, we can use some of those values and the sine function to find the area of an oblique triangle. Recall that the area formula for a triangle is given as where is base and is height. For oblique triangles, we must find before we can use the area formula. Observing the two triangles in [link] , one acute and one obtuse, we can drop a perpendicular to represent the height and then apply the trigonometric property to write an equation for area in oblique triangles. In the acute triangle, we have or However, in the obtuse triangle, we drop the perpendicular outside the triangle and extend the base to form a right triangle. The angle used in calculation is or

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Contemporary math applications' conversation and receive update notifications?