| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Platyhelminthes are traditionally divided into four classes: Turbellaria, Monogenea, Trematoda, and Cestoda ( [link] ). As discussed above, the relationships among members of these classes is being reassessed, with the turbellarians in particular now viewed as a paraphyletic group, a group that does not have a single common ancestor.
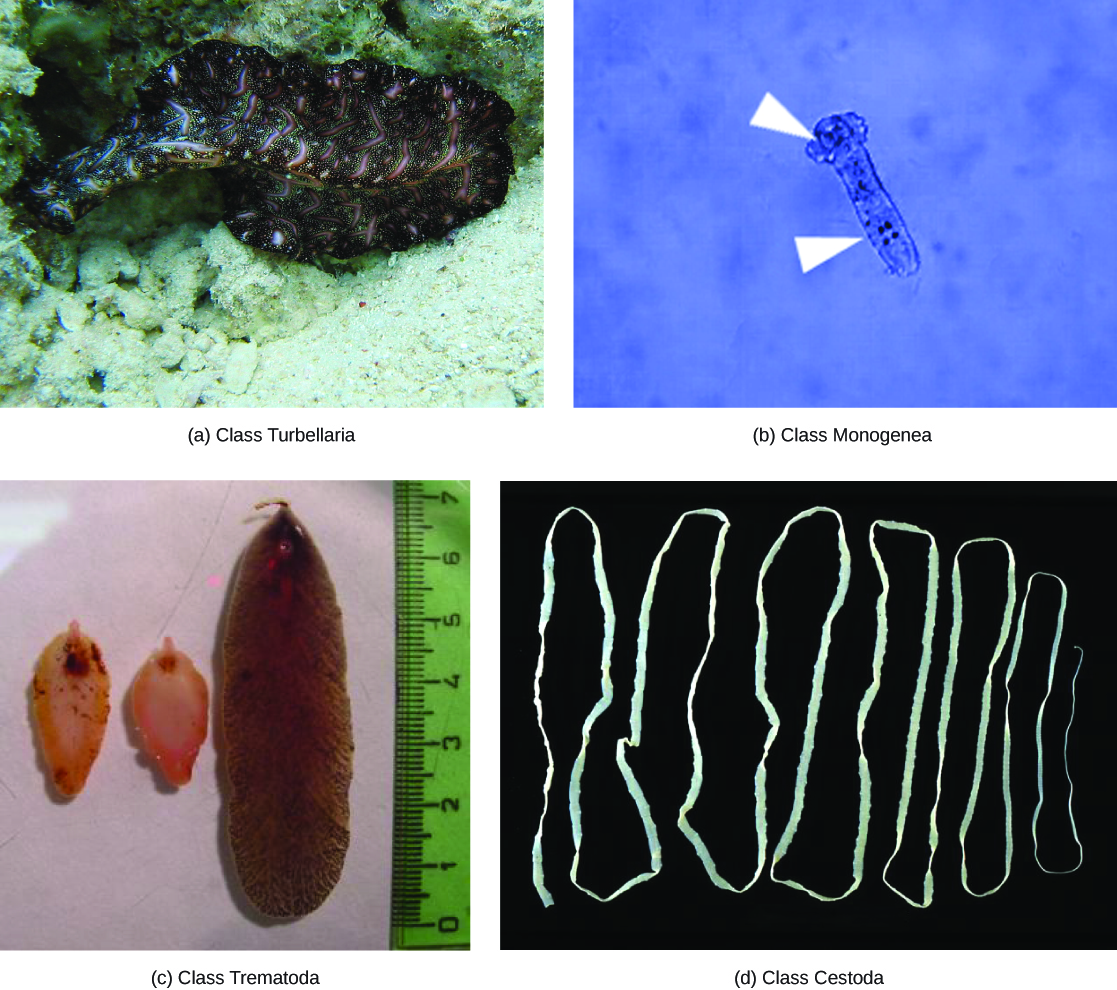
The class Turbellaria includes mainly free-living, marine species, although some species live in freshwater or moist terrestrial environments. The ventral epidermis of turbellarians is ciliated and facilitates their locomotion. Some turbellarians are capable of remarkable feats of regeneration in which they may regrow the body, even from a small fragment.
The monogeneans are ectoparasites, mostly of fish, with simple lifecycles that consist of a free-swimming larva that attaches to a fish to begin transformation to the parasitic adult form. The parasite has only one host and that host is usually only one species. The worms may produce enzymes that digest the host tissues or simply graze on surface mucus and skin particles. Most monogeneans are hermaphroditic, but the male gametes develop first and so cross-fertilization is quite common.
The trematodes, or flukes, are internal parasites of mollusks and many other groups, including humans. Trematodes have complex lifecycles that involve a primary host in which sexual reproduction occurs, and one or more secondary hosts in which asexual reproduction occurs. The primary host is almost always a mollusk. Trematodes are responsible for serious human diseases including schistosomiasis, a blood fluke. The disease infects an estimated 200 million people in the tropics, leading to organ damage and chronic symptoms like fatigue. Infection occurs when the human enters the water and a larva, released from the primary snail host, locates and penetrates the skin. The parasite infects various organs in the body and feeds on red blood cells before reproducing. Many of the eggs are released in feces and find their way into a waterway, where they are able to reinfect the primary snail host.
The cestodes, or tapeworms, are also internal parasites, mainly of vertebrates ( [link] ). Tapeworms live in the intestinal tract of the primary host and remain fixed using a sucker on the anterior end, or scolex, of the tapeworm body. The remaining body of the tapeworm is made up of a long series of units called proglottids, each of which may contain an excretory system with flame cells, but contain reproductive structures, both male and female. Tapeworms do not possess a digestive system; instead, they absorb nutrients from the food matter passing them in the host’s intestine.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Bi 101 for lbcc ilearn campus' conversation and receive update notifications?