| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
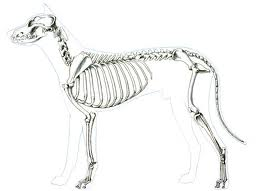
Water is about 1000 times denser than air and is a much more resistant medium to move through, its high density buoys up the body providing support.. One of themajor problems by animals moving from water to land was the increase in the force of gravity. In order to counter this, animals needed to develop stronglimbs and to adapt the skeleton to support their body weight on land.
Moving effectively on land is essential particularly if one needs to avoid predator, catch prey or adapt to a particular habitat.
Exposure to air results in evaporation of water from breathing organs and body surface. If this problem is not overcome animals will be confined to damphabitats
Constancy of temperature
Natural bodies of water do not show much temperature fluctuation, whereas on land, the range and fluctuation in temperatures can be large. This can causehuge problems for animals which have no temperature control mechanisms.
Gills depend on water flow or movement through water to operate. To survive on land a completely new mechanism of breathing needed to evolve.
The provision of safe shelter for the protection of vulnerable eggs and young is far easier on land than in water habitats.. The main problem here was to findmethods of reproduction which did not require fertilization in water
On land there are a tremendous variety of habitats e.g. tropical, coniferous and temperate forests, grasslands, deserts, mountains, oceanic islands and polarregions. Aquatic habitats, despite being far less diverse contain the greatest number and variety of living organisms on earth. Each habitat will havedifferent requirements with regard to access to food,, shelter, protection from enemies etc.
Arthropods moved onto the land long before the vertebrates emerged and a major factor in their success was the exoskeleton.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula: life sciences grade 10' conversation and receive update notifications?