| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
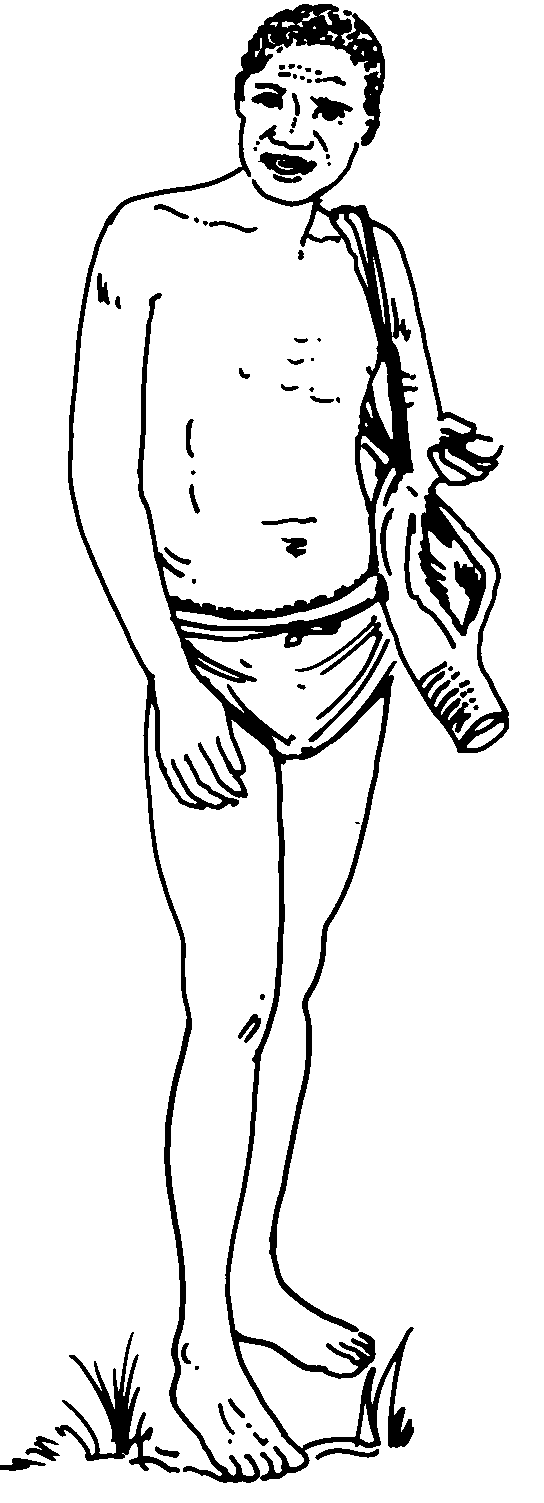
and _______________ (4) and the shaft was made from ___________ (5).
Poison from _____________ (6) and _____________ (7) was applied just behind the arrowhead.
The San carried their arrows in ______________ (8).
Small game and birds were caught in___________ (9)
and big game in_____________ (10).
“Welcome to the Khoina. It was the Europeans who changed our name to Hottentots, because we often used a word that sounded just like it. Apparently Khoina means ‘man of men’! Our diet , which was better than the San’s, helped us to develop a larger body frame.
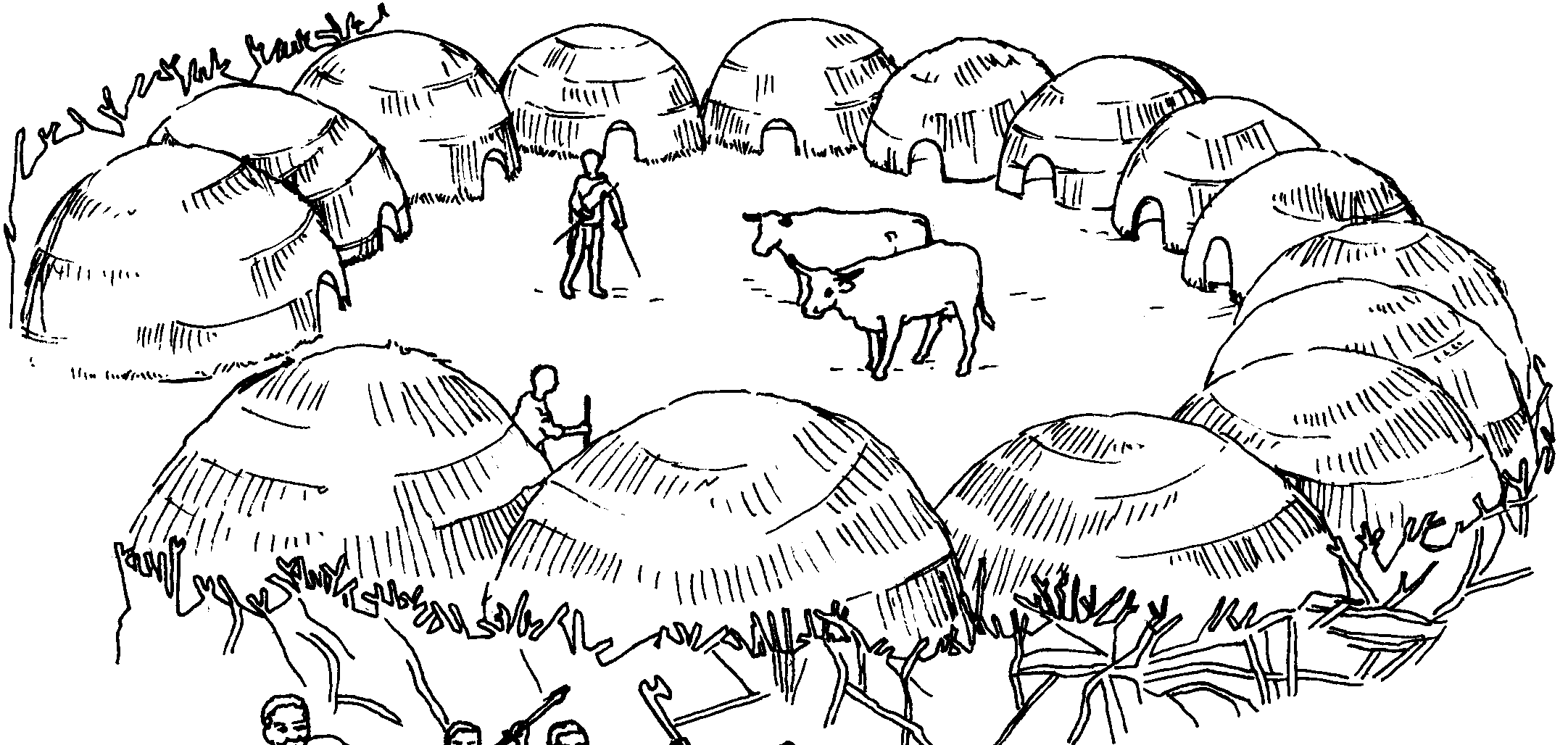
We arrived here from the north approximately 2 000 years ago. Before we moved southwards, we lived in the region that is known today as Botswana. Black people who moved through our territory taught us more about bartering and how to farm cattle in order to survive. The major difference between us and the San is that we are cattle farmers and they are hunter-gatherers. However, our appearance, language and customs show many similarities with those of the San. Contrary to the San, who move about in small hunting groups, the Khoina trek in large groups.
After the Dutch landed at the Cape with Jan van Riebeeck, we lost more and more of our grazing fields. In 1713 many Khoina died in the smallpox epidemic and we lost many of our cattle through various diseases. In order to survive, we were forced to find work on farms and in the towns, where many of our people intermarried with other groups. Today there are very few Khoina left. Most of them live in small groups in the Richtersveld as well as in Namibia (the Nama).”
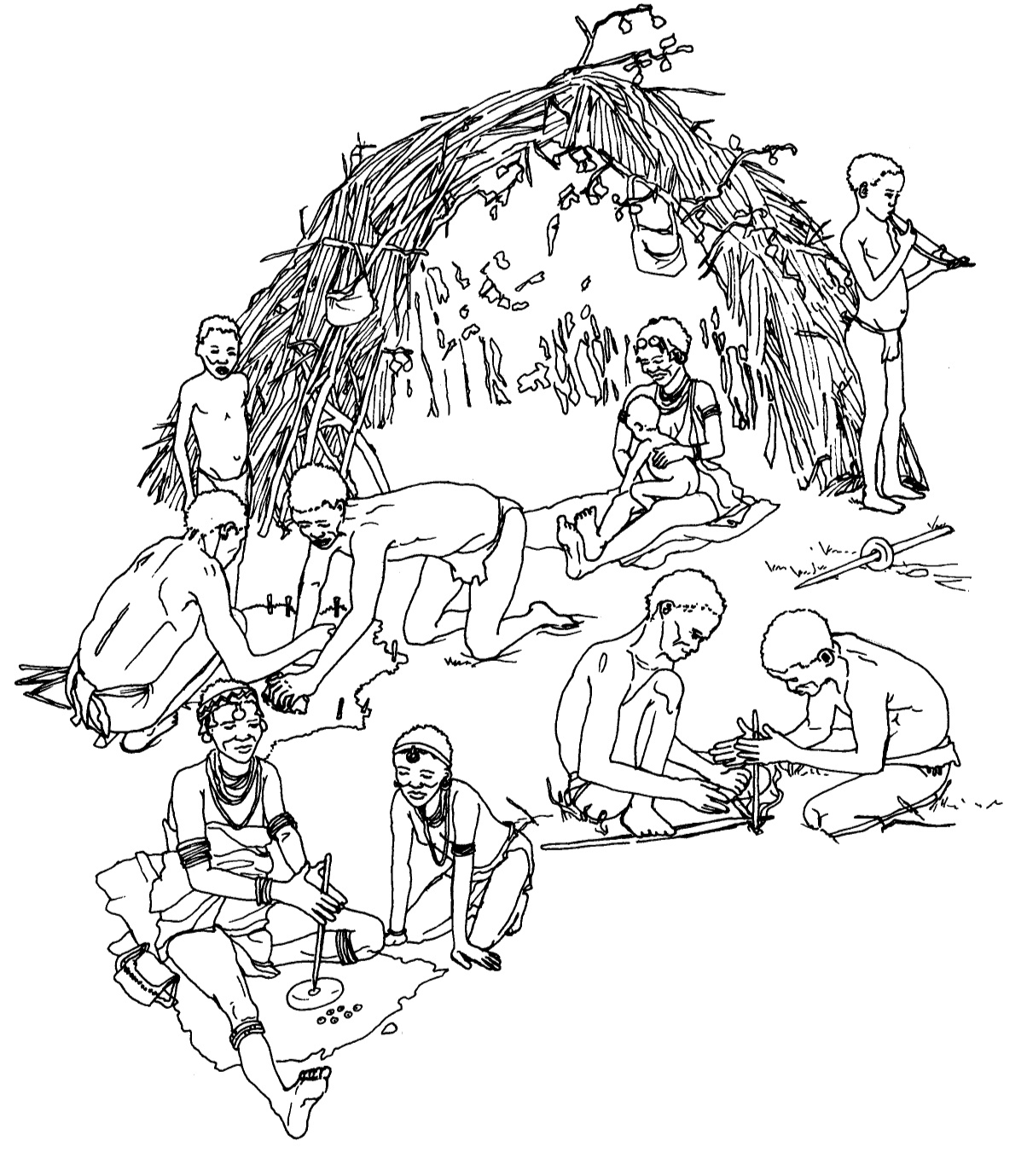


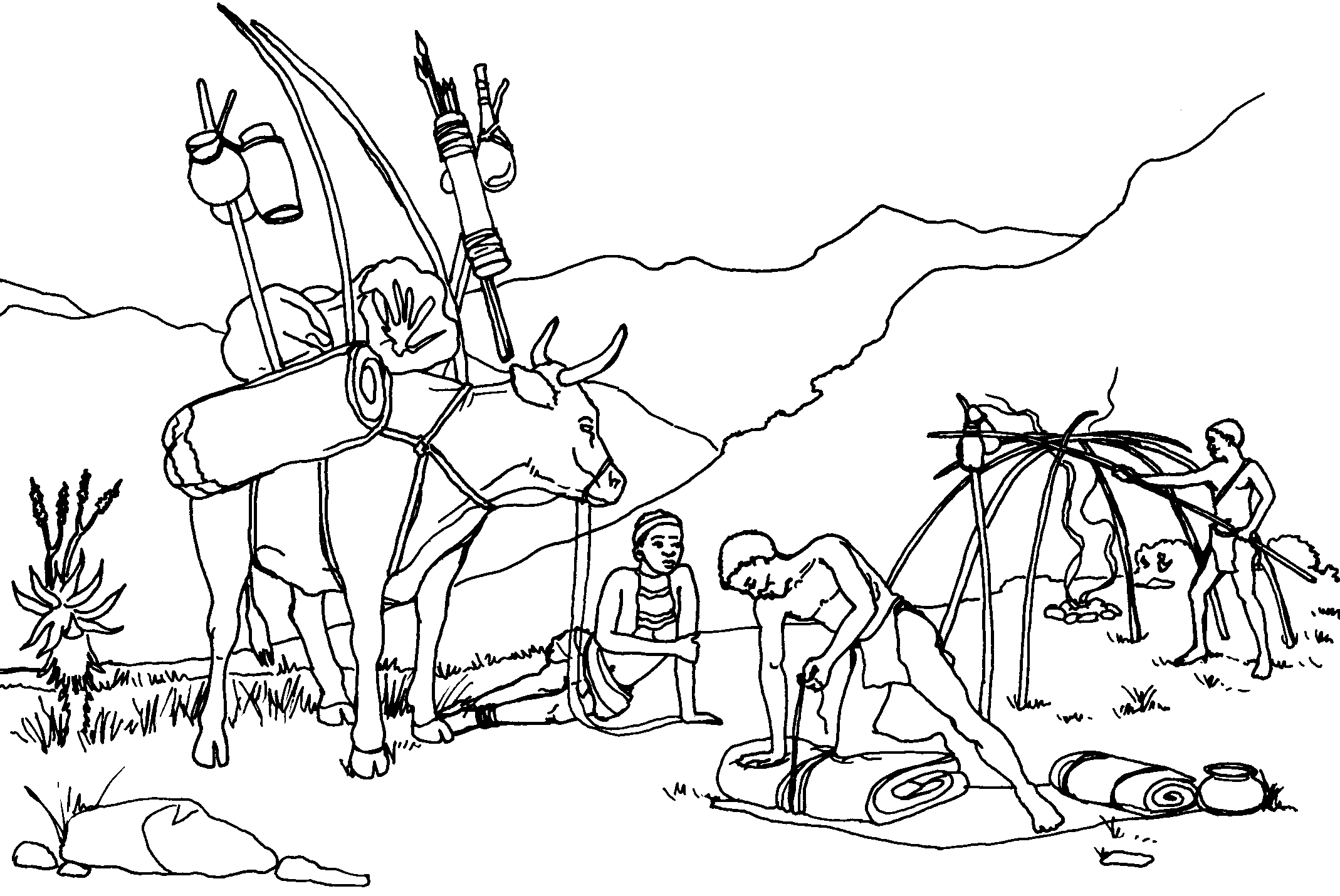
Customs
They were very fond of ______________ (2) and musical instruments.
Appearance
They were more powerfully built than ________________ (3).
Their clothes were made of sheep skins or the skins of ____________ (4) animals.
They liked decorations and adornments that were made of
________, __________ and ____________(5)
Dwellings
Their huts were built around the hut of the _______________ (6).
In the centre there was an open space for ______________ (7) at
night.
Reed mats were draped over a frame made of bent ________ (8).
Foods
More and more of them changed over to ______________ (9) farming.
They did not slaughter their ____________ (10) but they did slaughter sheep.
______________ (11) (a kind of milk) was one of their favourite
foods.
e) Now choose the correct answers from the frame below.

The Khoina kept __________ (1) or herds of _________(2). They realised that one can _______________ (3) animals and keep them in paddocks.
The Khoina had _____________ (4) and _____________ (5).These animals provided them with _____________ (6) and _____________(7).
They used ______________ (8) to ______________ (9) heavy loads. The Khoina regarded cattle as a sign of _______________ (10).
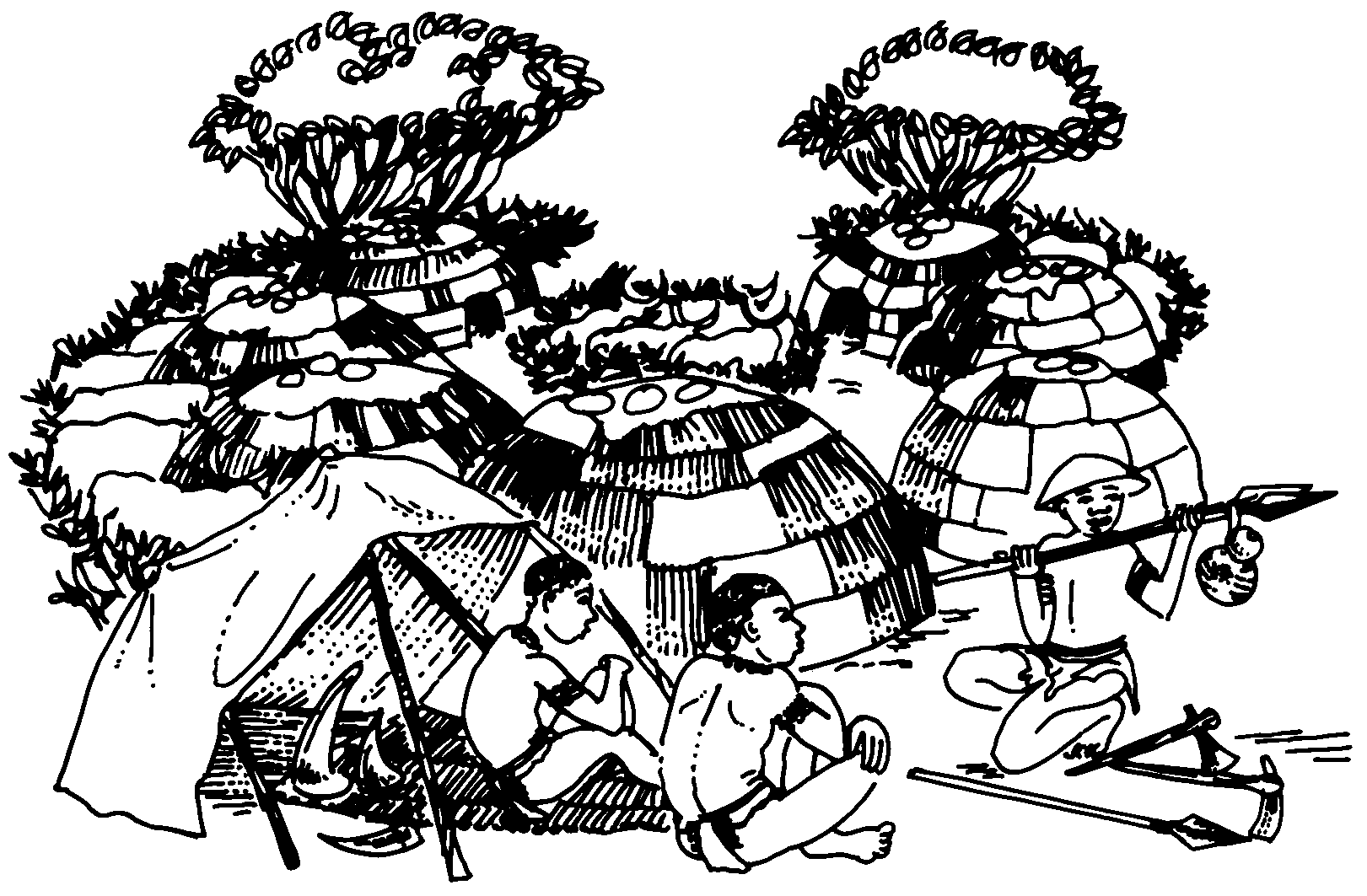
What is happening in the drawing?
When and where did it happen?
Why did it happen?
Do you recognise the people on the drawing? Can you find out what their names were?
How do we know that all of this really happened?
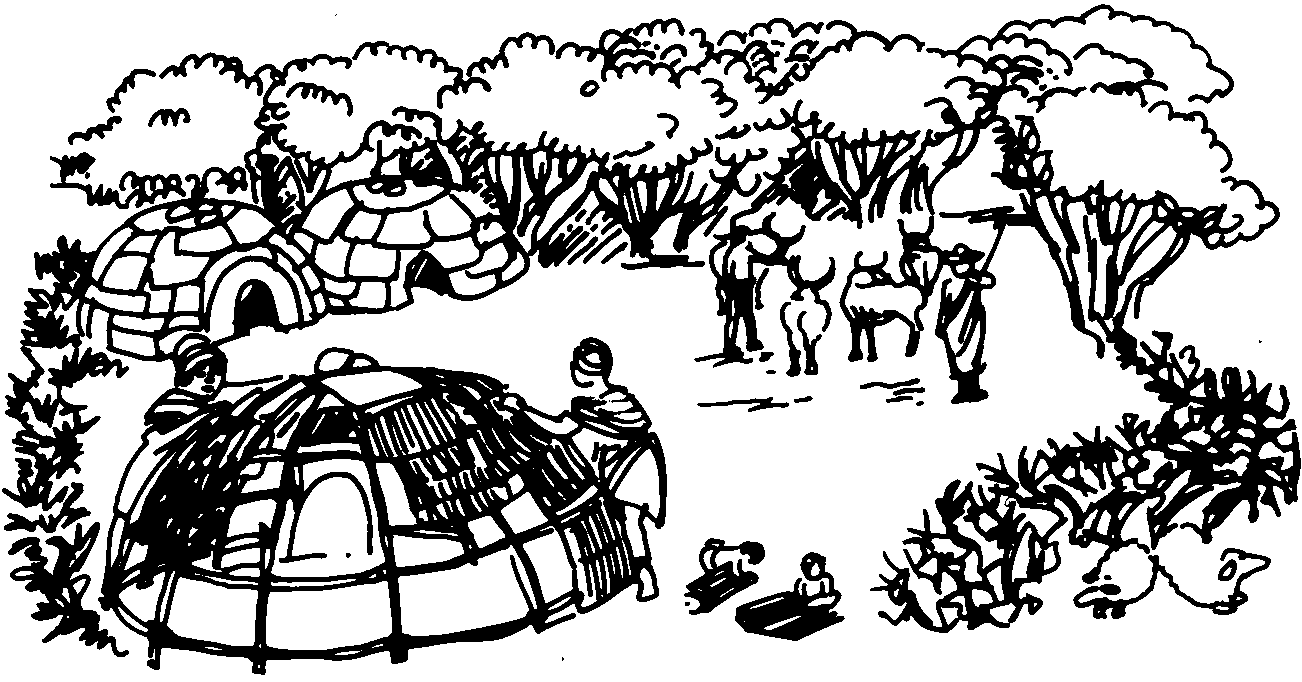

Why did the Khoina have more possessions than the San?
How were their huts built? What were the floors of the huts made of? What are the floors in your home made of?
Why were the huts built around the headman’s hut?
What did they sleep on at night? What do you sleep on?
Where did they get their water from? Where does your water supply at your home and your school come from?
| LO 3.3 |

LEARNING OUTCOME 3: INTERPRETING HISTORY – The learner will be able to interpret aspects of history
3.1 Be aware of more than one view of the past
Understand that different views of the same issue may be right or wrong.
3.2 Distinguish between fact and opinion.
Distinguish between a fact and an opinion.
Is able to access information from maps, charts, diagrams and graphs.
3.3 Reconstruct the past
Is able to reconstruct events and understand how people feel about them.
Activity
(a)
(i) 5
(ii) 5
(iii) 4
(iv) 1
(v) 2, 3
(b) Appearance: (1) ± 153 cm (2) fat (3) loin cloth (men), leather apron (women)
Customs: (4) moon (5) sitting
Tools: (6) bone, tortoise-shell, leaf, wood, stone
(c)
(d) Customs: (1) moon
(2) dance / song
Appearance: (3) the San
(4) wild animals
(5) seeds, berries, ostrich egg-shells, clay
Dwellings: (6) headman
(7) livestock (to sleep)
(8) thorntree branches and poles / slats
Foods: (9) livestock
(10) cattle
(11) Curdled milk (from calabashes)
(e)

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Social sciences: history grade 5' conversation and receive update notifications?