| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
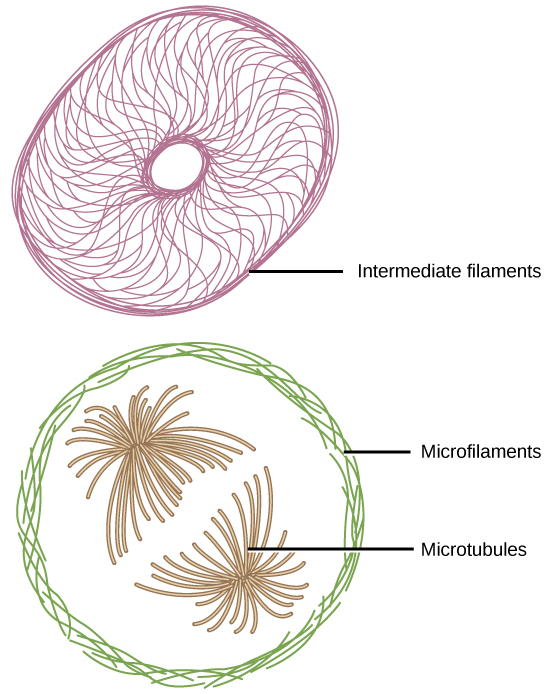
If you were to remove all the organelles from a cell, would the plasma membrane and the cytoplasm be the only components left? No. Within the cytoplasm, there would still be ions and organic molecules, plus a network of protein fibers that help maintain the shape of the cell, secure some organelles in specific positions, allow cytoplasm and vesicles to move within the cell, and enable cells within multicellular organisms to move. Collectively, this network of protein fibers is known as the cytoskeleton . There are three types of fibers within the cytoskeleton: microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules ( [link] ).
Of the three types of protein fibers in the cytoskeleton, microfilaments are the narrowest. They function in cellular movement, have a diameter of about 7 nm, and are made of two intertwined strands of a globular protein called actin ( [link] ). For this reason, microfilaments are also known as actin filaments.
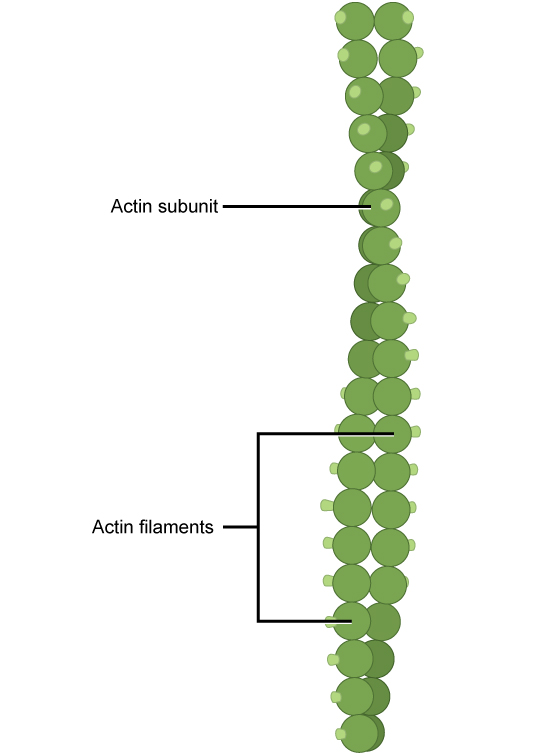
Microfilaments also provide some rigidity and shape to the cell. They can depolymerize (disassemble) and reform quickly, thus enabling a cell to change its shape and move. White blood cells (your body’s infection-fighting cells) make good use of this ability. They can move to the site of an infection and phagocytize the pathogen.
To see an example of a white blood cell in action, click here and watch a short time-lapse video of the cell capturing two bacteria. It engulfs one and then moves on to the other.
Intermediate filaments are made of several strands of fibrous proteins that are wound together ( [link] ). These elements of the cytoskeleton get their name from the fact that their diameter, 8 to 10 nm, is between those of microfilaments and microtubules.
Intermediate filaments have no role in cell movement. Their function is purely structural. They bear tension, thus maintaining the shape of the cell, and anchor the nucleus and other organelles in place. [link] shows how intermediate filaments create a supportive scaffolding inside the cell.
The intermediate filaments are the most diverse group of cytoskeletal elements. Several types of fibrous proteins are found in the intermediate filaments. You are probably most familiar with keratin, the fibrous protein that strengthens your hair, nails, and the epidermis of the skin.
As their name implies, microtubules are small hollow tubes. The walls of the microtubule are made of repeated tubulin proteins. With a diameter of about 25 nm, microtubules are the widest components of the cytoskeleton. They help the cell resist compression, provide a track along which vesicles move through the cell, and pull replicated chromosomes to opposite ends of a dividing cell. Like microfilaments, microtubules can dissolve and reform quickly.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'General biology part i - mixed majors' conversation and receive update notifications?