| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The reproductive tissues of male and female humans develop similarly in utero until about the seventh week of gestation when a low level of the hormone testosterone is released from the gonads of the developing male. Testosterone causes the primitive gonads to differentiate into male sexual organs. When testosterone is absent, the primitive gonads develop into ovaries. Tissues that produce a penis in males produce a clitoris in females. The tissue that will become the scrotum in a male becomes the labia in a female. Thus the male and female anatomies arise from a divergence in the development of what were once common embryonic structures.
Proper development of sperm cells requires a temperature slightly lower than the normal body temperature; therefore, the pair of testes must be suspended outside the pelvic cavity (in the scrotum) so the environment of the sperm is about 2 °C lower than body temperature. If the testes do not descend through the abdominal cavity during fetal development, the individual has reduced fertility.
The scrotum houses the testicles or testes (singular: testis), and provides passage for blood vessels, nerves, and muscles related to testicular function. The testes are a pair of male gonads that produce sperm and reproductive hormones. Coiled in each testis are seminiferous tubules, where sperm production begins.
The penis drains urine from the urinary bladder and is a copulatory organ during intercourse ( [link] ; [link] ). The penis contains three tubes of erectile tissue that become engorged with blood, making the penis erect, in preparation for intercourse. The organ is inserted into the vagina culminating with an ejaculation. During orgasm, the accessory organs and glands connected to the testes contract and empty the semen (containing sperm) into the urethra and the fluid is expelled from the body by muscular contractions causing ejaculation. After intercourse, the blood drains from the erectile tissue and the penis becomes flaccid.
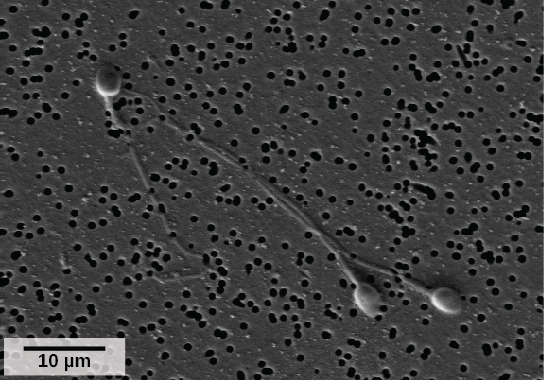
Semen is a mixture of sperm (about five percent of the total) and fluids from accessory glands (prostate, bulbourethral glands, and seminal vesicles) that contribute most of the semen’s volume. Sperm are haploid cells, consisting of a flagellum for movement, a neck that contains the cell’s energy-producing mitochondria, and a head that contains the genetic material ( [link] ). An acrosome (acrosomal vesicle) is found at the top of the head of the sperm. This structure contains enzymes that can digest the protective coverings that surround the egg and allow the sperm to fuse with the egg. An ejaculate will contain from two to five milliliters of fluid and from 50–120 million sperm per milliliter.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Human biology' conversation and receive update notifications?