| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
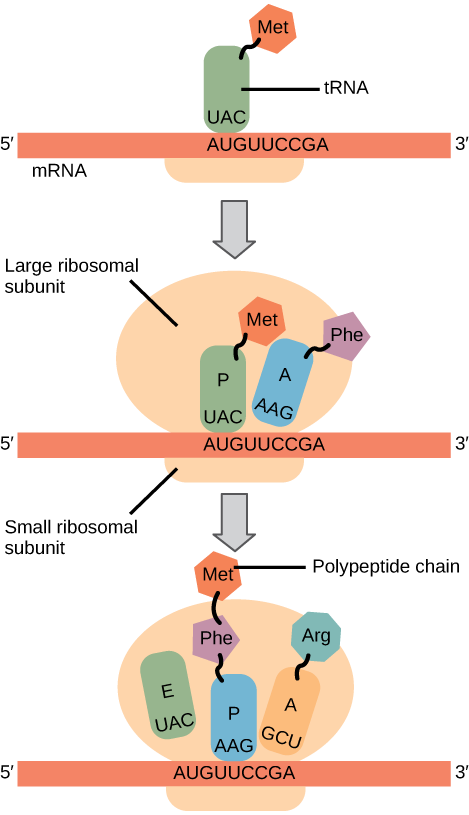
Elongation proceeds with charged tRNAs entering the A site and then shifting to the P site followed by the E site with each single-codon “step” of the ribosome. Ribosomal steps are induced by conformational changes that advance the ribosome by three bases in the 3' direction. The energy for each step of the ribosome is donated by an elongation factor that hydrolyzes GTP. Peptide bonds form between the amino group of the amino acid attached to the A-site tRNA and the carboxyl group of the amino acid attached to the P-site tRNA. The formation of each peptide bond is catalyzed by peptidyl transferase , an RNA-based enzyme that is integrated into the 50S ribosomal subunit. The energy for each peptide bond formation is derived from GTP hydrolysis, which is catalyzed by a separate elongation factor. The amino acid bound to the P-site tRNA is also linked to the growing polypeptide chain. As the ribosome steps across the mRNA, the former P-site tRNA enters the E site, detaches from the amino acid, and is expelled ( [link] ). Amazingly, the E. coli translation apparatus takes only 0.05 seconds to add each amino acid, meaning that a 200-amino acid protein can be translated in just 10 seconds.
Many antibiotics inhibit bacterial protein synthesis. For example, tetracycline blocks the A site on the bacterial ribosome, and chloramphenicol blocks peptidyl transfer. What specific effect would you expect each of these antibiotics to have on protein synthesis?
Tetracycline would directly affect:
Chloramphenicol would directly affect
Termination of translation occurs when a nonsense codon (UAA, UAG, or UGA) is encountered. Upon aligning with the A site, these nonsense codons are recognized by release factors in prokaryotes and eukaryotes that instruct peptidyl transferase to add a water molecule to the carboxyl end of the P-site amino acid. This reaction forces the P-site amino acid to detach from its tRNA, and the newly made protein is released. The small and large ribosomal subunits dissociate from the mRNA and from each other; they are recruited almost immediately into another translation initiation complex. After many ribosomes have completed translation, the mRNA is degraded so the nucleotides can be reused in another transcription reaction.
During and after translation, individual amino acids may be chemically modified, signal sequences may be appended, and the new protein “folds” into a distinct three-dimensional structure as a result of intramolecular interactions. A signal sequence is a short tail of amino acids that directs a protein to a specific cellular compartment. These sequences at the amino end or the carboxyl end of the protein can be thought of as the protein’s “train ticket” to its ultimate destination. Other cellular factors recognize each signal sequence and help transport the protein from the cytoplasm to its correct compartment. For instance, a specific sequence at the amino terminus will direct a protein to the mitochondria or chloroplasts (in plants). Once the protein reaches its cellular destination, the signal sequence is usually clipped off.
Many proteins fold spontaneously, but some proteins require helper molecules, called chaperones, to prevent them from aggregating during the complicated process of folding. Even if a protein is properly specified by its corresponding mRNA, it could take on a completely dysfunctional shape if abnormal temperature or pH conditions prevent it from folding correctly.
The players in translation include the mRNA template, ribosomes, tRNAs, and various enzymatic factors. The small ribosomal subunit forms on the mRNA template either at the Shine-Dalgarno sequence (prokaryotes) or the 5' cap (eukaryotes). Translation begins at the initiating AUG on the mRNA, specifying methionine. The formation of peptide bonds occurs between sequential amino acids specified by the mRNA template according to the genetic code. Charged tRNAs enter the ribosomal A site, and their amino acid bonds with the amino acid at the P site. The entire mRNA is translated in three-nucleotide “steps” of the ribosome. When a nonsense codon is encountered, a release factor binds and dissociates the components and frees the new protein. Folding of the protein occurs during and after translation.
[link] Many antibiotics inhibit bacterial protein synthesis. For example, tetracycline blocks the A site on the bacterial ribosome, and chloramphenicol blocks peptidyl transfer. What specific effect would you expect each of these antibiotics to have on protein synthesis?
Tetracycline would directly affect:
Chloramphenicol would directly affect
[link] Tetracycline: a; Chloramphenicol: c.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?