| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Maintaining homeostasis within the body requires the coordination of many different systems and organs. Communication between neighboring cells, and between cells and tissues in distant parts of the body, occurs through the release of chemicals called hormones. Hormones are released into body fluids (usually blood) that carry these chemicals to their target cells. At the target cells, which are cells that have a receptor for a signal or ligand from a signal cell, the hormones elicit a response. The cells, tissues, and organs that secrete hormones make up the endocrine system. Examples of glands of the endocrine system include the adrenal glands, which produce hormones such as epinephrine and norepinephrine that regulate responses to stress, and the thyroid gland, which produces thyroid hormones that regulate metabolic rates.
Although there are many different hormones in the human body, they can be divided into three classes based on their chemical structure: lipid-derived, amino acid-derived, and peptide (peptide and proteins) hormones. One of the key distinguishing features of lipid-derived hormones is that they can diffuse across plasma membranes whereas the amino acid-derived and peptide hormones cannot.
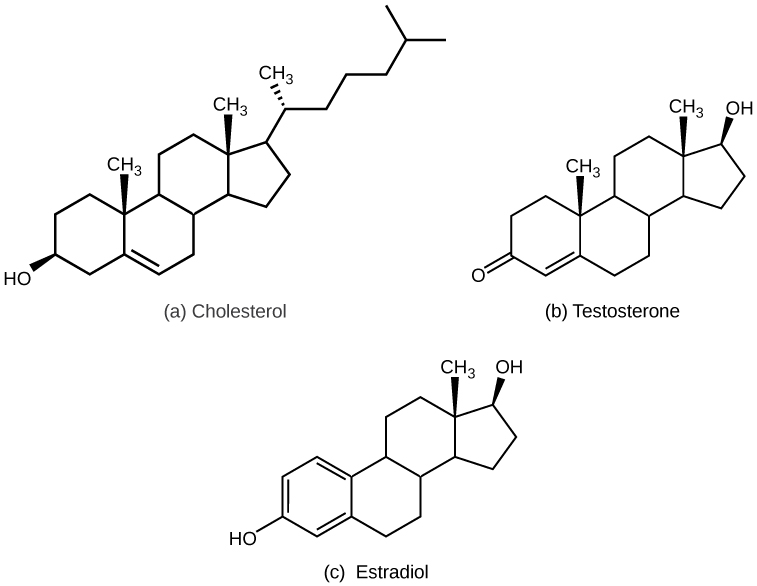
Most lipid hormones are derived from cholesterol and thus are structurally similar to it, as illustrated in [link] . The primary class of lipid hormones in humans is the steroid hormones. Chemically, these hormones are usually ketones or alcohols; their chemical names will end in “-ol” for alcohols or “-one” for ketones. Examples of steroid hormones include estradiol, which is an estrogen , or female sex hormone, and testosterone, which is an androgen, or male sex hormone. These two hormones are released by the female and male reproductive organs, respectively. Other steroid hormones include aldosterone and cortisol, which are released by the adrenal glands along with some other types of androgens. Steroid hormones are insoluble in water, and they are transported by transport proteins in blood. As a result, they remain in circulation longer than peptide hormones. For example, cortisol has a half-life of 60 to 90 minutes, while epinephrine, an amino acid derived-hormone, has a half-life of approximately one minute.
The amino acid-derived hormones are relatively small molecules that are derived from the amino acids tyrosine and tryptophan, shown in [link] . If a hormone is amino acid-derived, its chemical name will end in “-ine”. Examples of amino acid-derived hormones include epinephrine and norepinephrine, which are synthesized in the medulla of the adrenal glands, and thyroxine, which is produced by the thyroid gland. The pineal gland in the brain makes and secretes melatonin which regulates sleep cycles.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?