| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
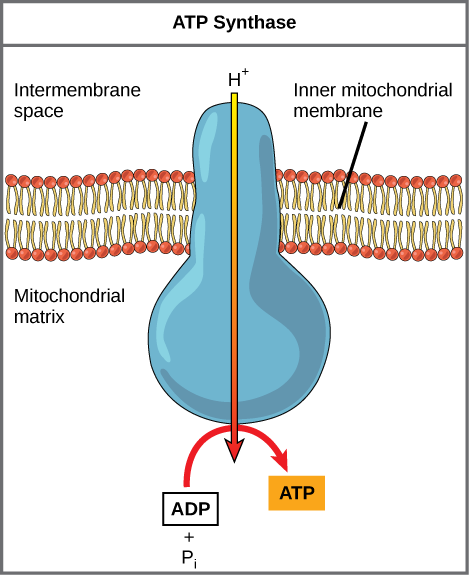
Dinitrophenol (DNP) is an uncoupler that makes the inner mitochondrial membrane leaky to protons. It was used until 1938 as a weight-loss drug. What effect would you expect DNP to have on the change in pH across the inner mitochondrial membrane? Why do you think this might be an effective weight-loss drug?
Chemiosmosis ( [link] ) is used to generate 90 percent of the ATP made during aerobic glucose catabolism; it is also the method used in the light reactions of photosynthesis to harness the energy of sunlight in the process of photophosphorylation. Recall that the production of ATP using the process of chemiosmosis in mitochondria is called oxidative phosphorylation. The overall result of these reactions is the production of ATP from the energy of the electrons removed from hydrogen atoms. These atoms were originally part of a glucose molecule. At the end of the pathway, the electrons are used to reduce an oxygen molecule to oxygen ions. The extra electrons on the oxygen attract hydrogen ions (protons) from the surrounding medium, and water is formed.
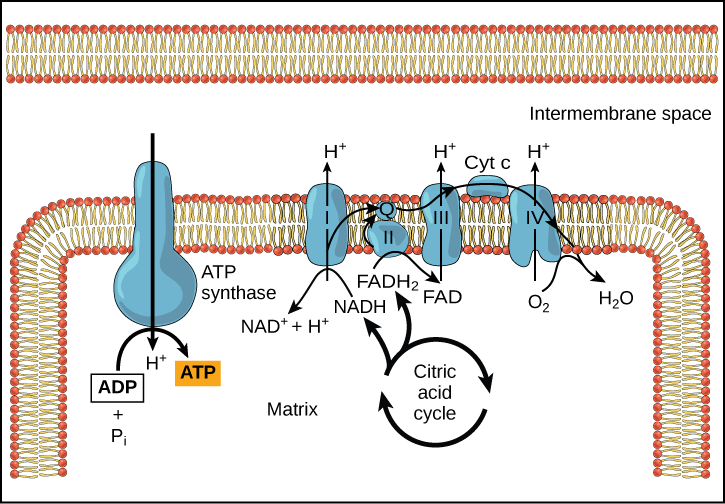
Cyanide inhibits cytochrome c oxidase, a component of the electron transport chain. If cyanide poisoning occurs, would you expect the pH of the intermembrane space to increase or decrease? What effect would cyanide have on ATP synthesis?
The number of ATP molecules generated from the catabolism of glucose varies. For example, the number of hydrogen ions that the electron transport chain complexes can pump through the membrane varies between species. Another source of variance stems from the shuttle of electrons across the membranes of the mitochondria. (The NADH generated from glycolysis cannot easily enter mitochondria.) Thus, electrons are picked up on the inside of mitochondria by either NAD + or FAD + . As you have learned earlier, these FAD + molecules can transport fewer ions; consequently, fewer ATP molecules are generated when FAD + acts as a carrier. NAD + is used as the electron transporter in the liver and FAD + acts in the brain.
Another factor that affects the yield of ATP molecules generated from glucose is the fact that intermediate compounds in these pathways are used for other purposes. Glucose catabolism connects with the pathways that build or break down all other biochemical compounds in cells, and the result is somewhat messier than the ideal situations described thus far. For example, sugars other than glucose are fed into the glycolytic pathway for energy extraction. Moreover, the five-carbon sugars that form nucleic acids are made from intermediates in glycolysis. Certain nonessential amino acids can be made from intermediates of both glycolysis and the citric acid cycle. Lipids, such as cholesterol and triglycerides, are also made from intermediates in these pathways, and both amino acids and triglycerides are broken down for energy through these pathways. Overall, in living systems, these pathways of glucose catabolism extract about 34 percent of the energy contained in glucose.
The electron transport chain is the portion of aerobic respiration that uses free oxygen as the final electron acceptor of the electrons removed from the intermediate compounds in glucose catabolism. The electron transport chain is composed of four large, multiprotein complexes embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane and two small diffusible electron carriers shuttling electrons between them. The electrons are passed through a series of redox reactions, with a small amount of free energy used at three points to transport hydrogen ions across a membrane. This process contributes to the gradient used in chemiosmosis. The electrons passing through the electron transport chain gradually lose energy, High-energy electrons donated to the chain by either NADH or FADH 2 complete the chain, as low-energy electrons reduce oxygen molecules and form water. The level of free energy of the electrons drops from about 60 kcal/mol in NADH or 45 kcal/mol in FADH 2 to about 0 kcal/mol in water. The end products of the electron transport chain are water and ATP. A number of intermediate compounds of the citric acid cycle can be diverted into the anabolism of other biochemical molecules, such as nonessential amino acids, sugars, and lipids. These same molecules can serve as energy sources for the glucose pathways.
[link] Dinitrophenol (DNP) is an uncoupler that makes the inner mitochondrial membrane leaky to protons. It was used until 1938 as a weight-loss drug. What effect would you expect DNP to have on the change in pH across the inner mitochondrial membrane? Why do you think this might be an effective weight-loss drug?
[link] After DNP poisoning, the electron transport chain can no longer form a proton gradient, and ATP synthase can no longer make ATP. DNP is an effective diet drug because it uncouples ATP synthesis; in other words, after taking it, a person obtains less energy out of the food he or she eats. Interestingly, one of the worst side effects of this drug is hyperthermia, or overheating of the body. Since ATP cannot be formed, the energy from electron transport is lost as heat.
[link] Cyanide inhibits cytochrome c oxidase, a component of the electron transport chain. If cyanide poisoning occurs, would you expect the pH of the intermembrane space to increase or decrease? What effect would cyanide have on ATP synthesis?
[link] After cyanide poisoning, the electron transport chain can no longer pump electrons into the intermembrane space. The pH of the intermembrane space would increase, the pH gradient would decrease, and ATP synthesis would stop.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Biology' conversation and receive update notifications?