| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
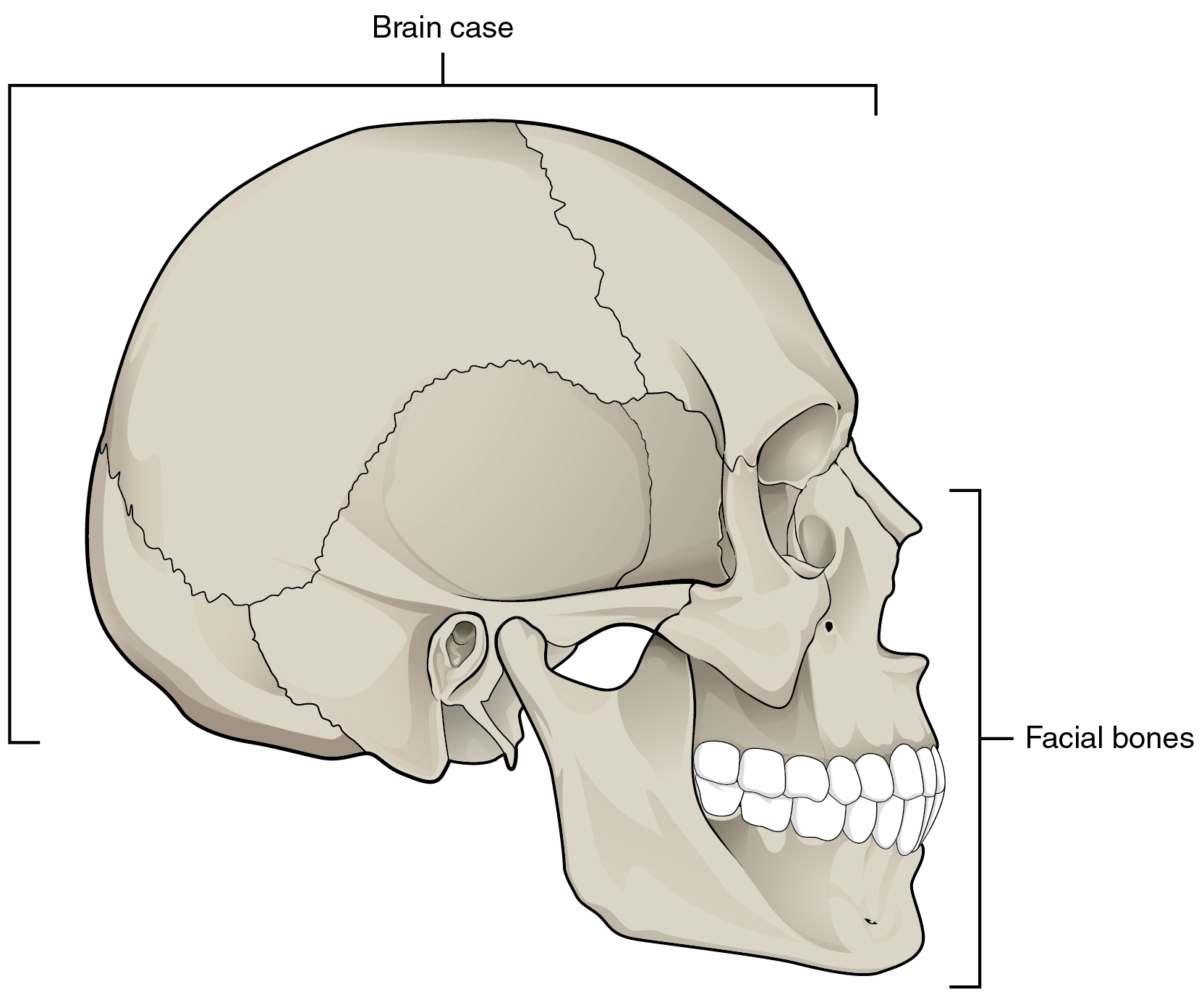
The cranium (skull) is the skeletal structure of the head that supports the face and protects the brain. It is subdivided into the facial bones and the brain case , or cranial vault ( [link] ). The facial bones underlie the facial structures, form the nasal cavity, enclose the eyeballs, and support the teeth of the upper and lower jaws. The rounded brain case surrounds and protects the brain and houses the middle and inner ear structures.
In the adult, the skull consists of 22 individual bones, 21 of which are immobile and united into a single unit. The 22nd bone is the mandible (lower jaw), which is the only moveable bone of the skull.
Watch this video to view a rotating and exploded skull, with color-coded bones. Which bone (yellow) is centrally located and joins with most of the other bones of the skull?
The anterior skull consists of the facial bones and provides the bony support for the eyes and structures of the face. This view of the skull is dominated by the openings of the orbits and the nasal cavity. Also seen are the upper and lower jaws, with their respective teeth ( [link] ).
The orbit is the bony socket that houses the eyeball and muscles that move the eyeball or open the upper eyelid. The upper margin of the anterior orbit is the supraorbital margin . Located near the midpoint of the supraorbital margin is a small opening called the supraorbital foramen . This provides for passage of a sensory nerve to the skin of the forehead. Below the orbit is the infraorbital foramen , which is the point of emergence for a sensory nerve that supplies the anterior face below the orbit.
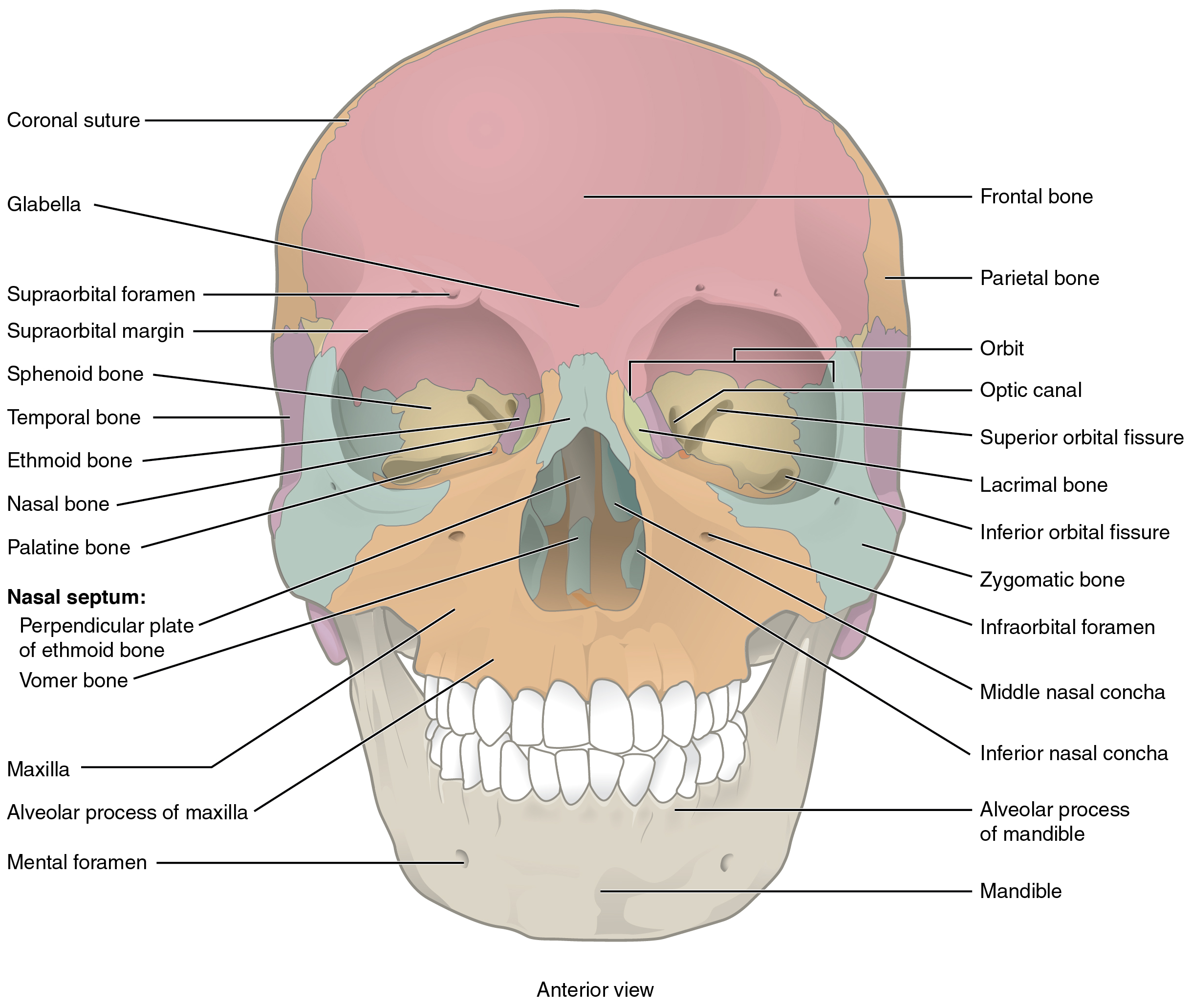
Inside the nasal area of the skull, the nasal cavity is divided into halves by the nasal septum . The upper portion of the nasal septum is formed by the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone and the lower portion is the vomer bone . Each side of the nasal cavity is triangular in shape, with a broad inferior space that narrows superiorly. When looking into the nasal cavity from the front of the skull, two bony plates are seen projecting from each lateral wall. The larger of these is the inferior nasal concha , an independent bone of the skull. Located just above the inferior concha is the middle nasal concha , which is part of the ethmoid bone. A third bony plate, also part of the ethmoid bone, is the superior nasal concha . It is much smaller and out of sight, above the middle concha. The superior nasal concha is located just lateral to the perpendicular plate, in the upper nasal cavity.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology' conversation and receive update notifications?