
|

4.1 Types of tissues Read Online
4.2 Epithelial tissue Read Online
4.3 Connective tissue supports and protects Read Online
4.4 Muscle tissue and motion Read Online
4.5 Nervous tissue mediates perception and response Read Online
After studying this chapter, you will be able to:
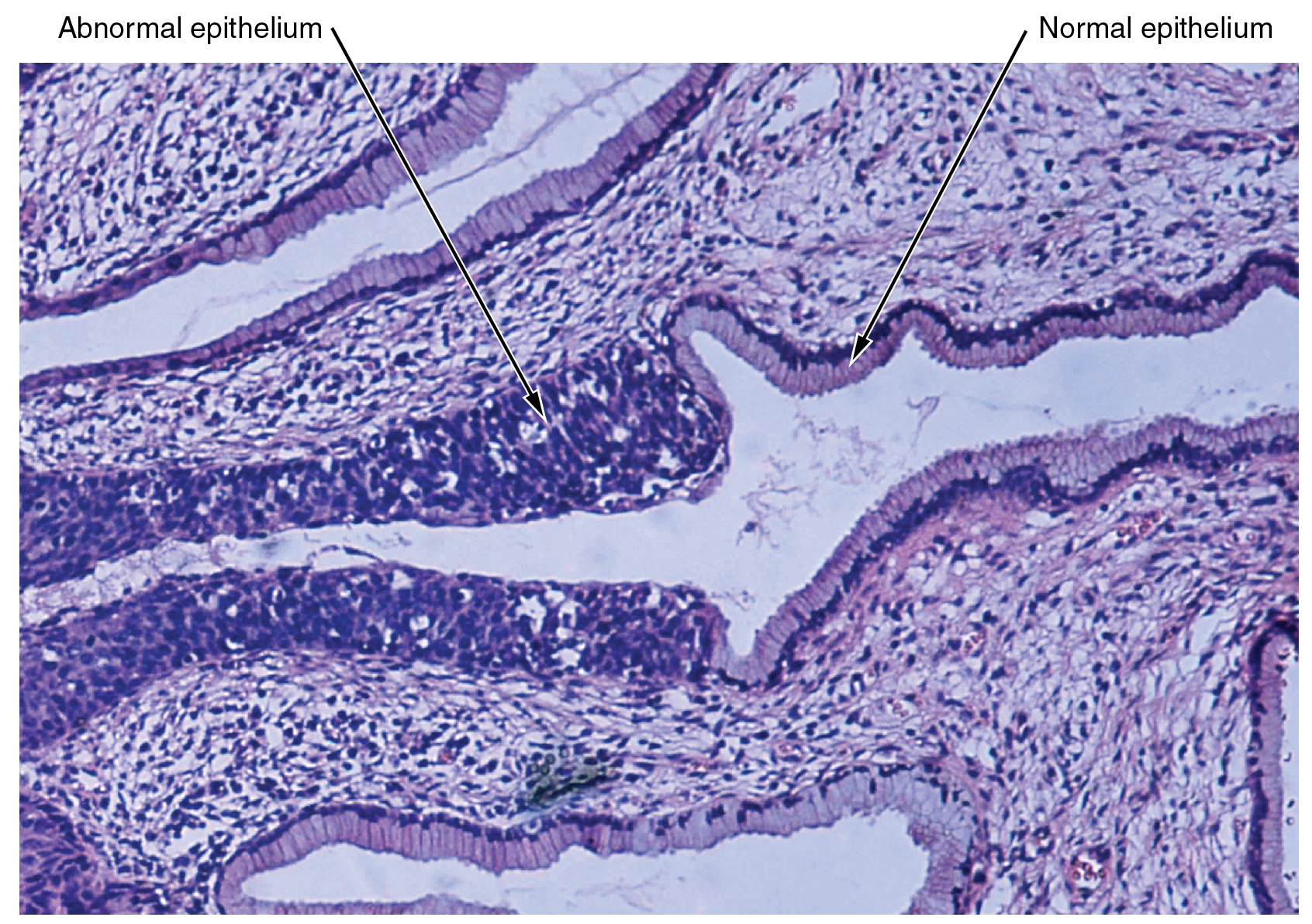
The body contains at least 200 distinct cell types. These cells contain essentially the same internal structures yet they vary enormously in shape and function. The different types of cells are not randomly distributed throughout the body; rather they occur in organized layers, a level of organization referred to as tissue. The micrograph that opens this chapter shows the high degree of organization among different types of cells in the tissue of the cervix. You can also see how that organization breaks down when cancer takes over the regular mitotic functioning of a cell.
The variety in shape reflects the many different roles that cells fulfill in your body. The human body starts as a single cell at fertilization. As this fertilized egg divides, it gives rise to trillions of cells, each built from the same blueprint, but organizing into tissues and becoming irreversibly committed to a developmental pathway.
Question: The process by which a less specialized cell matures into a more specialized cell is called ________.
Choices:
differentiation
maturation
modification
specialization
Question: Under the microscope, a tissue specimen shows cells located in spaces scattered in a transparent background. This is probably ________.
Choices:
loose connective tissue
a tendon
bone
hyaline cartilage
Question: Which of the following is not a type of tissue?
Choices:
muscle
nervous
embryonic
epithelial
Question: Differentiated cells in a developing embryo derive from ________.
Choices:
endothelium, mesothelium, and epithelium
ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm
connective tissue, epithelial tissue, and muscle tissue
epidermis, mesoderm, and endothelium
Question: Connective tissue is made of which three essential components?
Choices:
cells, ground substance, and carbohydrate fibers
cells, ground substance, and protein fibers
collagen, ground substance, and protein fibers
matrix, ground substance, and fluid
Question: The ________ exocrine gland stores its secretion until the glandular cell ruptures, whereas the ________ gland releases its apical region and reforms.
Choices:
holocrine; apocrine
eccrine; endocrine
apocrine; holocrine
eccrine; apocrine
Question: Which connective tissue specializes in storage of fat?
Choices:
tendon
adipose tissue
reticular tissue
dense connective tissue
Question: Which of the following is the epithelial tissue that lines the interior of blood vessels?
Choices:
columnar
pseudostratified
simple squamous
transitional
Question: In observing epithelial cells under a microscope, the cells are arranged in a single layer and look tall and narrow, and the nucleus is located close to the basal side of the cell. The specimen is what type of epithelial tissue?
Choices:
columnar
stratified
squamous
transitional
Question: Which of the following lines the body cavities exposed to the external environment?
Choices:
mesothelium
lamina propria
mesenteries
mucosa
Question: Which type of epithelial tissue specializes in moving particles across its surface and is found in airways and lining of the oviduct?
Choices:
transitional
stratified columnar
pseudostratified ciliated columnar
stratified squamous