| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Before you get started, take this readiness quiz.
We have used the Distributive Property to simplify expressions like . You multiplied both terms in the parentheses, , by 2, to get . With this chapter’s new vocabulary, you can say you were multiplying a binomial, , by a monomial, 2.
Multiplying a binomial by a monomial is nothing new for you! Here’s an example:
Multiply:
| The monomial is the second factor. |
 |
| Distribute. |
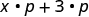 |
| Simplify. |
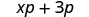 |
Just like there are different ways to represent multiplication of numbers, there are several methods that can be used to multiply a binomial times a binomial. We will start by using the Distributive Property.
Look at [link] , where we multiplied a binomial by a monomial .
 | |
| We distributed the p to get: |
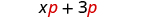 |
| What if we have ( x + 7) instead of p ? |
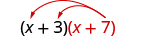 |
| Distribute ( x + 7). |
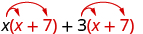 |
| Distribute again. |
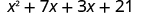 |
| Combine like terms. |
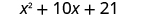 |
Notice that before combining like terms, you had four terms. You multiplied the two terms of the first binomial by the two terms of the second binomial—four multiplications.
Multiply:
 | |
| Distribute ( y + 8). |
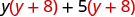 |
| Distribute again |
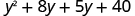 |
| Combine like terms. |
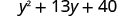 |
Multiply:
 | |
| Distribute (3 y + 4). |
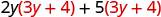 |
| Distribute again |
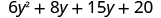 |
| Combine like terms. |
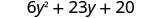 |
Multiply:
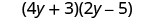 | |
| Distribute. |
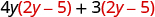 |
| Distribute again. |
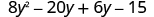 |
| Combine like terms. |
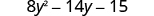 |
Multiply:
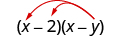 | |
| Distribute. |
 |
| Distribute again. |
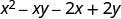 |
| There are no like terms to combine. |
Remember that when you multiply a binomial by a binomial you get four terms. Sometimes you can combine like terms to get a trinomial , but sometimes, like in [link] , there are no like terms to combine.
Let’s look at the last example again and pay particular attention to how we got the four terms.
Where did the first term, , come from?

We abbreviate “First, Outer, Inner, Last” as FOIL. The letters stand for ‘ F irst, O uter, I nner, L ast’. The word FOIL is easy to remember and ensures we find all four products.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Elementary algebra' conversation and receive update notifications?