| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Also during the Cold War, global inequality was described in terms of economic development. Along with developing and developed nations, the terms less-developed nation and underdeveloped nation were used. This was the era when the idea of noblesse oblige (first-world responsibility) took root, suggesting that the so-termed developed nations should provide foreign aid to the less-developed and underdeveloped nations in order to raise their standard of living.
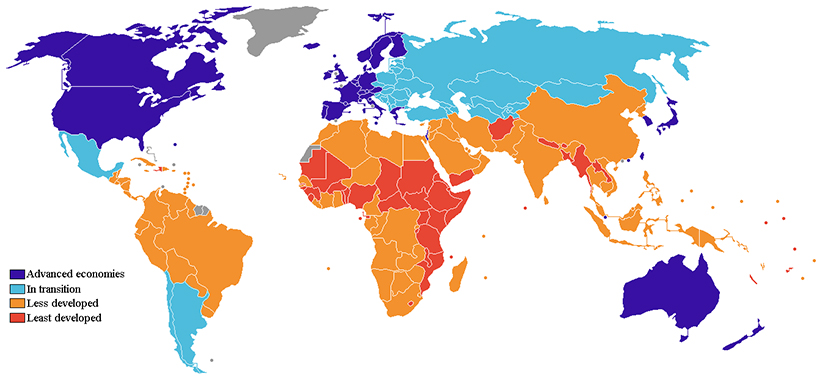
Immanuel Wallerstein’s (1979) world systems approach uses an economic basis to understand global inequality. Wallerstein conceived of the global economy as a complex system that supports an economic hierarchy that placed some nations in positions of power with numerous resources and other nations in a state of economic subordination. Those that were in a state of subordination faced significant obstacles to mobilization.
Core nations are dominant capitalist countries, highly industrialized, technological, and urbanized. For example, Wallerstein contends that the United States is an economic powerhouse that can support or deny support to important economic legislation with far-reaching implications, thus exerting control over every aspect of the global economy and exploiting both semi-peripheral and peripheral nations. We can look at free trade agreements such as the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) as an example of how a core nation is able to leverage its power to gain the most advantageous position in the matter of global trade.
Peripheral nations have very little industrialization; what they do have often represents the outdated castoffs of core nations or the factories and means of production owned by core nations. They typically have unstable governments, inadequate social programs, and are economically dependent on core nations for jobs and aid. There are abundant examples of countries in this category, such as Vietnam and Cuba. We can be sure the workers in a Cuban cigar factory, for example, which are owned or leased by global core nation companies, are not enjoying the same privileges and rights as U.S. workers.
Semi-peripheral nations are in-between nations, not powerful enough to dictate policy but nevertheless acting as a major source for raw material and an expanding middle-class marketplace for core nations, while also exploiting peripheral nations. Mexico is an example, providing abundant cheap agricultural labor to the U.S., and supplying goods to the United States market at a rate dictated by the U.S. without the constitutional protections offered to United States workers.
While the World Bank is often criticized, both for its policies and its method of calculating data, it is still a common source for global economic data.
Along with tracking the economy, the World Bank tracks demographics and environmental health to provide a complete picture of whether a nation is high income, middle income, or low income.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Introduction to sociology 2e' conversation and receive update notifications?