| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
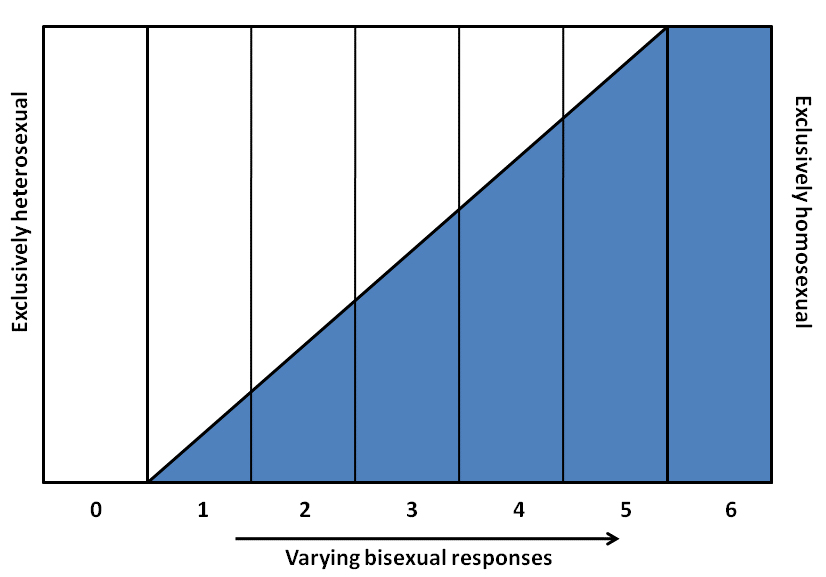
Alfred Kinsey was among the first to conceptualize sexuality as a continuum rather than a strict dichotomy of gay or straight. He created a six-point rating scale that ranges from exclusively heterosexual to exclusively homosexual. See the figure below. In his 1948 work Sexual Behavior in the Human Male , Kinsey writes, “Males do not represent two discrete populations, heterosexual and homosexual. The world is not to be divided into sheep and goats … The living world is a continuum in each and every one of its aspects” (Kinsey 1948).
Later scholarship by Eve Kosofsky Sedgwick expanded on Kinsey’s notions. She coined the term “homosocial” to oppose “homosexual,” describing nonsexual same-sex relations. Sedgwick recognized that in U.S. culture, males are subject to a clear divide between the two sides of this continuum, whereas females enjoy more fluidity. This can be illustrated by the way women in the United States can express homosocial feelings (nonsexual regard for people of the same sex) through hugging, handholding, and physical closeness. In contrast, U.S. males refrain from these expressions since they violate the heteronormative expectation that male sexual attraction should be exclusively for females. Research suggests that it is easier for women violate these norms than men, because men are subject to more social disapproval for being physically close to other men (Sedgwick 1985).
There is no scientific consensus regarding the exact reasons why an individual holds a heterosexual, homosexual, or bisexual orientation. Research has been conducted to study the possible genetic, hormonal, developmental, social, and cultural influences on sexual orientation, but there has been no evidence that links sexual orientation to one factor (APA 2008). Research, however, does present evidence showing that homosexuals and bisexuals are treated differently than heterosexuals in schools, the workplace, and the military. In 2011, for example, Sears and Mallory used General Social Survey data from 2008 to show that 27 percent of lesbian, gay, bisexual (LGB) respondents reported experiencing sexual orientation-based discrimination during the five years prior to the survey. Further, 38 percent of openly LGB people experienced discrimination during the same time.
Much of this discrimination is based on stereotypes and misinformation. Some is based on heterosexism , which Herek (1990) suggests is both an ideology and a set of institutional practices that privilege heterosexuals and heterosexuality over other sexual orientations. Much like racism and sexism, heterosexism is a systematic disadvantage embedded in our social institutions, offering power to those who conform to hetereosexual orientation while simultaneously disadvantaging those who do not. Homophobia , an extreme or irrational aversion to homosexuals, accounts for further stereotyping and discrimination. Major policies to prevent discrimination based on sexual orientation have not come into effect until the last few years. In 2011, President Obama overturned “don’t ask, don’t tell,” a controversial policy that required homosexuals in the US military to keep their sexuality undisclosed. The Employee Non-Discrimination Act, which ensures workplace equality regardless of sexual orientation, is still pending full government approval. Organizations such as GLAAD (Gay&Lesbian Alliance Against Defamation) advocate for homosexual rights and encourage governments and citizens to recognize the presence of sexual discrimination and work to prevent it. Other advocacy agencies frequently use the acronyms LBGT and LBGTQ, which stands for “Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Transgender” (and “Queer” or “Questioning” when the Q is added).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Introduction to sociology 2e' conversation and receive update notifications?