| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Cognitive therapy was developed by psychiatrist Aaron Beck in the 1960s. His initial focus was on depression and how a client’s self-defeating attitude served to maintain a depression despite positive factors in her life (Beck, Rush, Shaw,&Emery, 1979) ( [link] ). Through questioning, a cognitive therapist can help a client recognize dysfunctional ideas, challenge catastrophizing thoughts about themselves and their situations, and find a more positive way to view things (Beck, 2011).
View a brief video in which Judith Beck talks about cognitive therapy and conducts a session with a client.
Cognitive-behavioral therapists focus much more on present issues than on a patient’s childhood or past, as in other forms of psychotherapy. One of the first forms of cognitive-behavioral therapy was rational emotive therapy (RET) , which was founded by Albert Ellis and grew out of his dislike of Freudian psychoanalysis (Daniel, n.d.). Behaviorists such as Joseph Wolpe also influenced Ellis’s therapeutic approach (National Association of Cognitive-Behavioral Therapists, 2009).
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) helps clients examine how their thoughts affect their behavior. It aims to change cognitive distortions and self-defeating behaviors. In essence, this approach is designed to change the way people think as well as how they act. It is similar to cognitive therapy in that CBT attempts to make individuals aware of their irrational and negative thoughts and helps people replace them with new, more positive ways of thinking. It is also similar to behavior therapies in that CBT teaches people how to practice and engage in more positive and healthy approaches to daily situations. In total, hundreds of studies have shown the effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy in the treatment of numerous psychological disorders such as depression, PTSD, anxiety disorders, eating disorders, bipolar disorder, and substance abuse (Beck Institute for Cognitive Behavior Therapy, n.d.). For example, CBT has been found to be effective in decreasing levels of hopelessness and suicidal thoughts in previously suicidal teenagers (Alavi, Sharifi, Ghanizadeh,&Dehbozorgi, 2013). Cognitive-behavioral therapy has also been effective in reducing PTSD in specific populations, such as transit workers (Lowinger&Rombom, 2012).
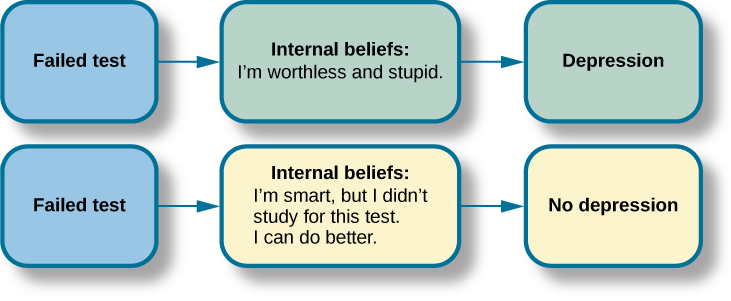
Cognitive-behavioral therapy aims to change cognitive distortions and self-defeating behaviors using techniques like the ABC model. With this model, there is an A ction (sometimes called an activating event), the B elief about the event, and the C onsequences of this belief. Let’s say, Jon and Joe both go to a party. Jon and Joe each have met a young woman at the party: Jon is talking with Megan most of the party, and Joe is talking with Amanda. At the end of the party, Jon asks Megan for her phone number and Joe asks Amanda. Megan tells Jon she would rather not give him her number, and Amanda tells Joe the same thing. Both Jon and Joe are surprised, as they thought things were going well. What can Jon and Joe tell themselves about why the women were not interested? Let’s say Jon tells himself he is a loser, or is ugly, or “has no game.” Jon then gets depressed and decides not to go to another party, which starts a cycle that keeps him depressed. Joe tells himself that he had bad breath, goes out and buys a new toothbrush, goes to another party, and meets someone new.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Psychology' conversation and receive update notifications?