| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The visual system constructs a mental representation of the world around us ( [link] ). This contributes to our ability to successfully navigate through physical space and interact with important individuals and objects in our environments. This section will provide an overview of the basic anatomy and function of the visual system. In addition, we will explore our ability to perceive color and depth.

The eye is the major sensory organ involved in vision ( [link] ). Light waves are transmitted across the cornea and enter the eye through the pupil. The cornea is the transparent covering over the eye. It serves as a barrier between the inner eye and the outside world, and it is involved in focusing light waves that enter the eye. The pupil is the small opening in the eye through which light passes, and the size of the pupil can change as a function of light levels as well as emotional arousal. When light levels are low, the pupil will become dilated, or expanded, to allow more light to enter the eye. When light levels are high, the pupil will constrict, or become smaller, to reduce the amount of light that enters the eye. The pupil’s size is controlled by muscles that are connected to the iris , which is the colored portion of the eye.
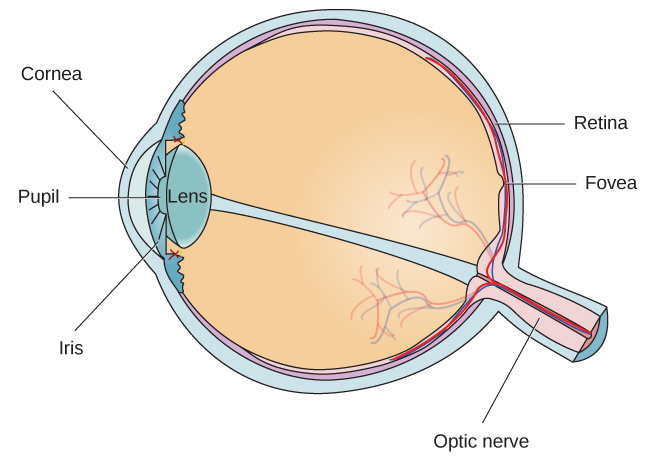
After passing through the pupil, light crosses the lens , a curved, transparent structure that serves to provide additional focus. The lens is attached to muscles that can change its shape to aid in focusing light that is reflected from near or far objects. In a normal-sighted individual, the lens will focus images perfectly on a small indentation in the back of the eye known as the fovea , which is part of the retina , the light-sensitive lining of the eye. The fovea contains densely packed specialized photoreceptor cells ( [link] ). These photoreceptor cells, known as cones, are light-detecting cells. The cones are specialized types of photoreceptors that work best in bright light conditions. Cones are very sensitive to acute detail and provide tremendous spatial resolution. They also are directly involved in our ability to perceive color.
While cones are concentrated in the fovea, where images tend to be focused, rods, another type of photoreceptor, are located throughout the remainder of the retina. Rods are specialized photoreceptors that work well in low light conditions, and while they lack the spatial resolution and color function of the cones, they are involved in our vision in dimly lit environments as well as in our perception of movement on the periphery of our visual field.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Psychology' conversation and receive update notifications?