| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Although the study of stress and how it affects us physically and psychologically is fascinating, it is—admittedly—somewhat of a grim topic. Psychology is also interested in the study of a more upbeat and encouraging approach to human affairs—the quest for happiness.
America’s founders declared that its citizens have an unalienable right to pursue happiness. But what is happiness? When asked to define the term, people emphasize different aspects of this elusive state. Indeed, happiness is somewhat ambiguous and can be defined from different perspectives (Martin, 2012). Some people, especially those who are highly committed to their religious faith, view happiness in ways that emphasize virtuosity, reverence, and enlightened spirituality. Others see happiness as primarily contentment—the inner peace and joy that come from deep satisfaction with one’s surroundings, relationships with others, accomplishments, and oneself. Still others view happiness mainly as pleasurable engagement with their personal environment—having a career and hobbies that are engaging, meaningful, rewarding, and exciting. These differences, of course, are merely differences in emphasis. Most people would probably agree that each of these views, in some respects, captures the essence of happiness.
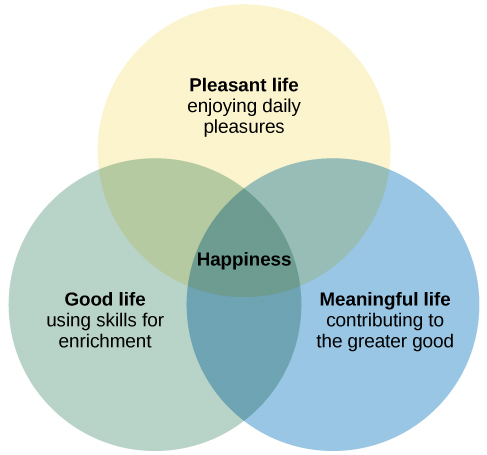
Some psychologists have suggested that happiness consists of three distinct elements: the pleasant life, the good life, and the meaningful life, as shown in [link] (Seligman, 2002; Seligman, Steen, Park,&Peterson, 2005). The pleasant life is realized through the attainment of day-to-day pleasures that add fun, joy, and excitement to our lives. For example, evening walks along the beach and a fulfilling sex life can enhance our daily pleasure and contribute to the pleasant life. The good life is achieved through identifying our unique skills and abilities and engaging these talents to enrich our lives; those who achieve the good life often find themselves absorbed in their work or their recreational pursuits. The meaningful life involves a deep sense of fulfillment that comes from using our talents in the service of the greater good: in ways that benefit the lives of others or that make the world a better place. In general, the happiest people tend to be those who pursue the full life—they orient their pursuits toward all three elements (Seligman et al., 2005).
For practical purposes, a precise definition of happiness might incorporate each of these elements: an enduring state of mind consisting of joy, contentment, and other positive emotions, plus the sense that one’s life has meaning and value (Lyubomirsky, 2001). The definition implies that happiness is a long-term state—what is often characterized as subjective well-being—rather than merely a transient positive mood we all experience from time to time. It is this enduring happiness that has captured the interests of psychologists and other social scientists.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Psychology' conversation and receive update notifications?