| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
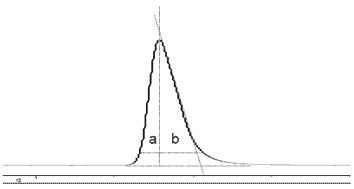
The attributions of an ideal separation are as follows:
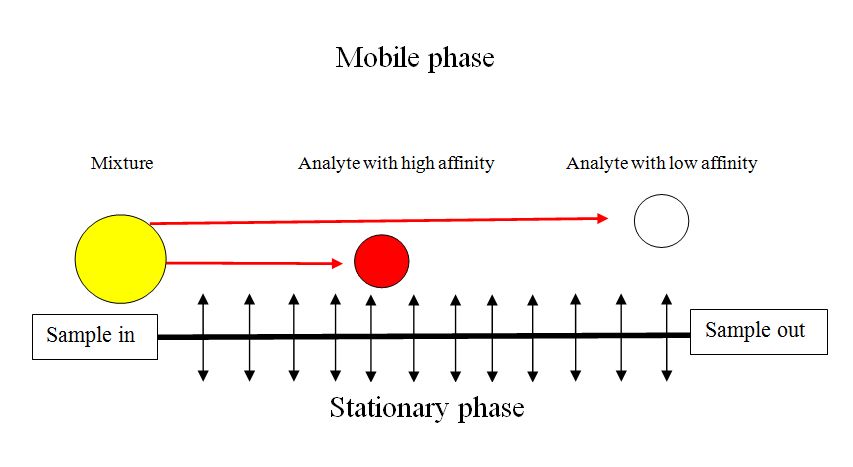
In its simplest form gas chromatography is a process whereby a sample is vaporized and injected onto the chromatographic column, where it is separated into its many components. The elution is brought about by the flow of carrier gas ( [link] ). The carrier gas serves as the mobile phase that elutes the components of a mixture from a column containing an immobilized stationary phase. In contrast to most other types of chromatography, the mobile phase does not interact with molecules of the analytes. Carrier gases, the mobile phase of GC, include helium, hydrogen and nitrogen which are chemically inert. The stationary phase in gas-solid chromatography is a solid that has a large surface area at which adsorption of the analyte species (solutes) take place. In gas-liquid chromatography, a stationary phase is liquid that is immobilized on the surface of a solid support by adsorption or by chemical bonding.
Gas chromatographic separation occurs because of differences in the positions of adsorption equilibrium between the gaseous components of the sample and the stationary phases ( [link] ). In GC the distribution ratio (ratio of the concentration of analytes in stationary and mobile phase) is dependent on the component vapor pressure, the thermodynamic properties of the bulk component band and affinity for the stationary phase. The equilibrium is temperature dependent. Hence the importance of the selection the stationary phase of the column and column temperature programming in optimizing a separation.
Helium, nitrogen, argon, hydrogen and air are typically used carrier gases. Which one is used is usually determined by the detector being used, for example, a discharge ionization detection (DID) requires helium as the carrier gas. When analyzing gas samples, however, the carrier is sometimes selected based on the sample's matrix, for example, when analyzing a mixture in argon, an argon carrier is preferred, because the argon in the sample does not show up on the chromatogram. Safety and availability are other factors, for example, hydrogen is flammable, and high-purity helium can be difficult to obtain in some areas of the world.
The carrier gas flow rate affects the analysis in the same way that temperature does. The higher the flow rate the faster the analysis, but the lower the separation between analytes. Furthermore, the shape of peak will be also effected by the flow rate. The slower the rate is, the more axial and radical diffusion are, the broader and the more asymmetric the peak is. Selecting the flow rate is therefore the same compromise between the level of separation and length of analysis as selecting the column temperature.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physical methods in chemistry and nano science' conversation and receive update notifications?