| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
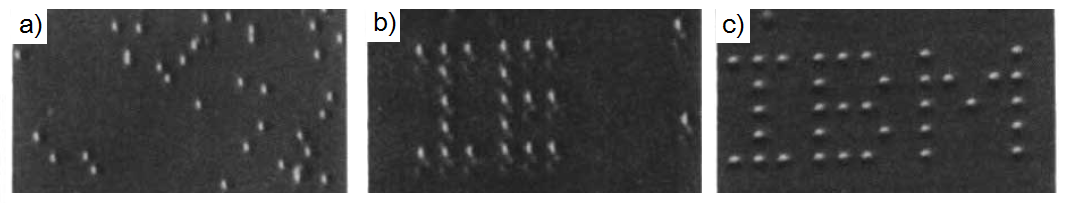
As single molecule imaging methods such as scanning tunneling microscope (STM), atomic force microscope (AFM), and transmission electron microscope (TEM) developed in the past decades, scientists have gained powerful tools to explore molecular structures and behaviors in previously unknown areas. Among these imaging methods, STM is probably the most suitable one to observe detail at molecular level. STM can operate in a wide range of conditions, provides very high resolution, and able to manipulate molecular motions with the tip. An interesting early example came from IBM in 1990, in which the STM was used to position individual atoms for the first time, spelling out "I-B-M" in Xenon atoms. This work revealed that observation and control of single atoms and molecular motions on surfaces were possible.
The IBM work, and subsequent experiments, relied on the fact that STM tip always exerts a finite force toward an adsorbate atom that contains both van der Waals and electrostatic forces was utilized for manipulation purpose. By adjusting the position and the voltage of the tip, the interactions between the tip and the target molecule were changed. Therefore, applying/releasing force to a single atom and make it move was possible [link] .
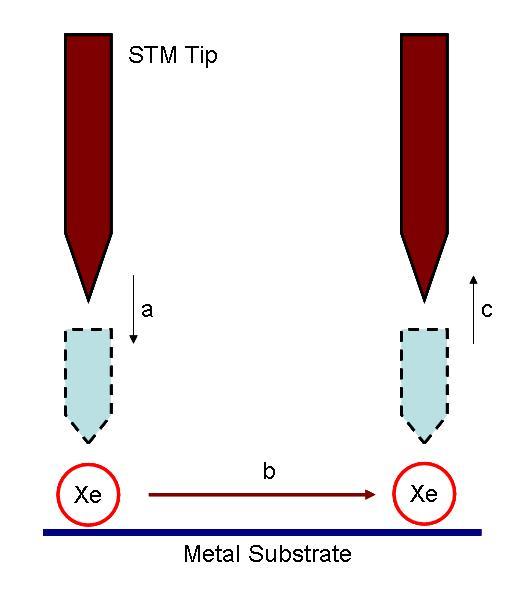
The actual positioning experiment was carried out in the following process. The nickel metal substrate was prepared by cycles of argon-ion sputtering, followed by annealing in a partial pressure of oxygen to remove surface carbon and other impurities. After the cleaning process, the sample was cooled to 4 K, and imaged with the STM to ensure the quality of surface. The nickel sample was then doped with xenon. An image of the doped sample was taken at constant-current scanning conditions. Each xenon atom appears as a located randomly 1.6 Å high bump on the surface ( [link] a). Under the imaging conditions (tip bias = 0.010 V with tunneling current 10 -9 A) the interaction of the xenon with the tip is too weak to cause the position of the xenon atom to be perturbed. To move an atom, the STM tip was placed on top of the atom performing the procedure depicted in [link] to move it to its target. Repeating this process again and again led the researcher to build of the structure they desired [link] b and c.
All motions on surfaces at the single molecule level can be described as by the following (or combination of the following) modes:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physical methods in chemistry and nano science' conversation and receive update notifications?