| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
One of the main research interests of the semiconductor industry is to improve the performance of semiconducting devices and to construct new materials with reduced size or thickness that have potential application in transistors and microelectronic devices. However, the most significant challenge regarding thin film semiconductor materials is measurement. Properties such as the thickness, composition at the surface, and contamination, all are critical parameters of the thin films. To address these issues, we need an analytical technique which can measure accurately through the depth of the of the semiconductor surface without destruction of the material. Rutherford backscattering spectroscopy is a unique analysis method for this purpose. It can give us information regarding in-depth profiling in a non-destructive manner. However X-ray photo electron spectroscopy (XPS), energy dispersive X-ray analysis (EDX) and Auger electron spectroscopy are also able to study the depth-profile of semiconductor films. [link] demonstrates the comparison between those techniques with RBS.
| Method | Destructive | Incident particle | Outgoing Particle | Detection limit | Depth resolution |
| RBS | No | Ion | Ion | ~1 | 10 nm |
| XPS | Yes | X-ray photon | Electron | ~0.1-1 | ~1 µm |
| EDX | Yes | Electron | X-ray photon | ~0.1 | 1.5 nm |
| Auger | Yes | Electron | Electron | ~0.1-1 | 1.5 nm |
At a basic level, RBS demonstrates the electrostatic repulsion between high energy incident ions and target nuclei. The specimen under study is bombarded with monoenergetic beam of 4 He + particles and the backscattered particles are detected by the detector-analysis system which measures the energies of the particles. During the collision, energy is transferred from the incident particle to the target specimen atoms; the change in energy of the scattered particle depends on the masses of incoming and target atoms. For an incident particle of mass M 1 , the energy is E 0 while the mass of the target atom is M 2 . After the collision, the residual energy E of the particle scattered at angle Ø can be expressed as:
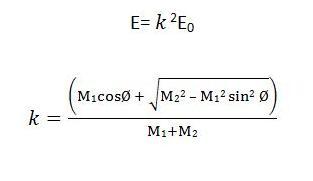
where k is the kinematic scattering factor, which is actually the energy ratio of the particle before and after the collision. Since k depends on the masses of the incident particle and target atom and the scattering angle, the energy of the scattered particle is also determined by these three parameters. A simplified layout of backscattering experiment is shown in Figure 1 .
The probability of a scattering event can be described by the differential scattering cross section of a target atom for scattering an incoming particle through the angle Ø into differential solid angle as follows,
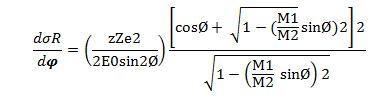
where d σ R is the effective differential cross section for the scattering of a particle. The above equation may looks complicated but it conveys the message that the probability of scattering event can be expressed as a function of scattering cross section which is proportional to the zZ when a particle with charge ze approaches the target atom with charge Ze.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Physical methods in chemistry and nano science' conversation and receive update notifications?