| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In Bohr’s model of the hydrogen atom, the electron moves in a circular orbit around the proton. The electron passes by a particular point on the loop in a certain time, so we can calculate a current . An electron that orbits a proton in a hydrogen atom is therefore analogous to current flowing through a circular wire ( [link] ). In the study of magnetism, we saw that a current-carrying wire produces magnetic fields. It is therefore reasonable to conclude that the hydrogen atom produces a magnetic field and interacts with other magnetic fields.
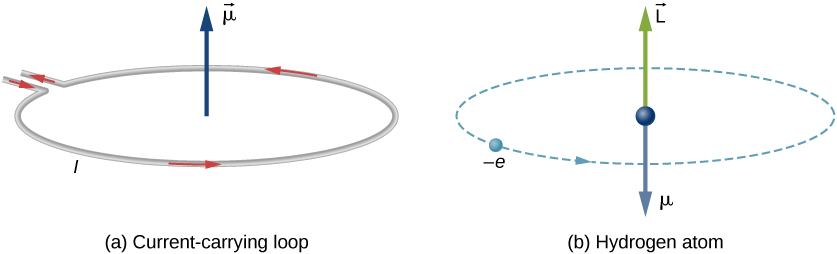
The orbital magnetic dipole moment is a measure of the strength of the magnetic field produced by the orbital angular momentum of an electron. From Force and Torque on a Current Loop , the magnitude of the orbital magnetic dipole moment for a current loop is
where I is the current and A is the area of the loop. (For brevity, we refer to this as the magnetic moment.) The current I associated with an electron in orbit about a proton in a hydrogen atom is
where e is the magnitude of the electron charge and T is its orbital period. If we assume that the electron travels in a perfectly circular orbit, the orbital period is
where r is the radius of the orbit and v is the speed of the electron in its orbit. Given that the area of a circle is , the absolute magnetic moment is
It is helpful to express the magnetic momentum in terms of the orbital angular momentum Because the electron orbits in a circle, the position vector and the momentum vector form a right angle. Thus, the magnitude of the orbital angular momentum is
Combining these two equations, we have
In full vector form, this expression is written as
The negative sign appears because the electron has a negative charge. Notice that the direction of the magnetic moment of the electron is antiparallel to the orbital angular momentum, as shown in [link] (b). In the Bohr model of the atom, the relationship between and in [link] is independent of the radius of the orbit.
The magnetic moment can also be expressed in terms of the orbital angular quantum number l . Combining [link] and [link] , the magnitude of the magnetic moment is
The z -component of the magnetic moment is
The quantity is a fundamental unit of magnetism called the Bohr magneton , which has the value (J/T) or Quantization of the magnetic moment is the result of quantization of the orbital angular momentum.
As we will see in the next section, the total magnetic dipole moment of the hydrogen atom is due to both the orbital motion of the electron and its intrinsic spin. For now, we ignore the effect of electron spin.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?