| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Historically, Bohr’s model of the hydrogen atom is the very first model of atomic structure that correctly explained the radiation spectra of atomic hydrogen. The model has a special place in the history of physics because it introduced an early quantum theory, which brought about new developments in scientific thought and later culminated in the development of quantum mechanics. To understand the specifics of Bohr’s model, we must first review the nineteenth-century discoveries that prompted its formulation.
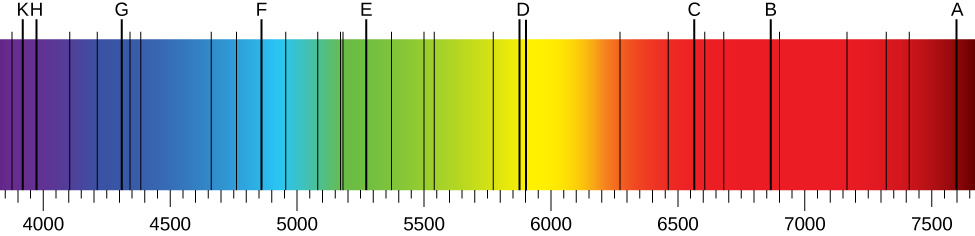
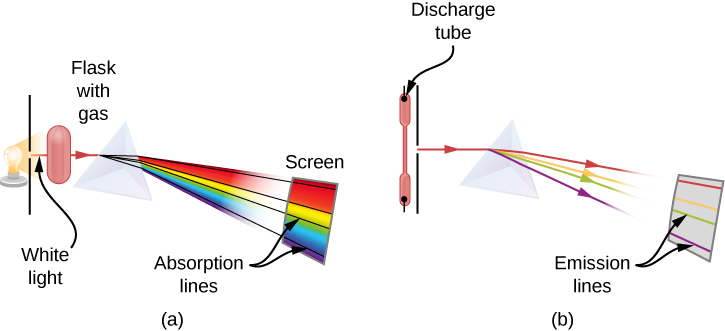
When we use a prism to analyze white light coming from the sun, several dark lines in the solar spectrum are observed ( [link] ). Solar absorption lines are called Fraunhofer lines after Joseph von Fraunhofer , who accurately measured their wavelengths. During 1854–1861, Gustav Kirchhoff and Robert Bunsen discovered that for the various chemical elements, the line emission spectrum of an element exactly matches its line absorption spectrum . The difference between the absorption spectrum and the emission spectrum is explained in [link] . An absorption spectrum is observed when light passes through a gas. This spectrum appears as black lines that occur only at certain wavelengths on the background of the continuous spectrum of white light ( [link] ). The missing wavelengths tell us which wavelengths of the radiation are absorbed by the gas. The emission spectrum is observed when light is emitted by a gas. This spectrum is seen as colorful lines on the black background (see [link] and [link] ). Positions of the emission lines tell us which wavelengths of the radiation are emitted by the gas. Each chemical element has its own characteristic emission spectrum. For each element, the positions of its emission lines are exactly the same as the positions of its absorption lines. This means that atoms of a specific element absorb radiation only at specific wavelengths and radiation that does not have these wavelengths is not absorbed by the element at all. This also means that the radiation emitted by atoms of each element has exactly the same wavelengths as the radiation they absorb.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?