| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
All bodies emit electromagnetic radiation over a range of wavelengths. In an earlier chapter, we learned that a cooler body radiates less energy than a warmer body. We also know by observation that when a body is heated and its temperature rises, the perceived wavelength of its emitted radiation changes from infrared to red, and then from red to orange, and so forth. As its temperature rises, the body glows with the colors corresponding to ever-smaller wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum. This is the underlying principle of the incandescent light bulb: A hot metal filament glows red, and when heating continues, its glow eventually covers the entire visible portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. The temperature ( T ) of the object that emits radiation, or the emitter , determines the wavelength at which the radiated energy is at its maximum. For example, the Sun, whose surface temperature is in the range between 5000 K and 6000 K, radiates most strongly in a range of wavelengths about 560 nm in the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum. Your body, when at its normal temperature of about 300 K, radiates most strongly in the infrared part of the spectrum.
Radiation that is incident on an object is partially absorbed and partially reflected. At thermodynamic equilibrium, the rate at which an object absorbs radiation is the same as the rate at which it emits it. Therefore, a good absorber of radiation (any object that absorbs radiation) is also a good emitter. A perfect absorber absorbs all electromagnetic radiation incident on it; such an object is called a blackbody .
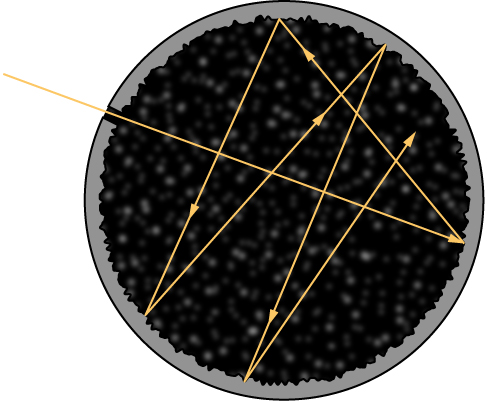
Although the blackbody is an idealization, because no physical object absorbs 100% of incident radiation, we can construct a close realization of a blackbody in the form of a small hole in the wall of a sealed enclosure known as a cavity radiator, as shown in [link] . The inside walls of a cavity radiator are rough and blackened so that any radiation that enters through a tiny hole in the cavity wall becomes trapped inside the cavity. At thermodynamic equilibrium (at temperature T ), the cavity walls absorb exactly as much radiation as they emit. Furthermore, inside the cavity, the radiation entering the hole is balanced by the radiation leaving it. The emission spectrum of a blackbody can be obtained by analyzing the light radiating from the hole. Electromagnetic waves emitted by a blackbody are called blackbody radiation .
The intensity of blackbody radiation depends on the wavelength of the emitted radiation and on the temperature T of the blackbody ( [link] ). The function is the power intensity that is radiated per unit wavelength; in other words, it is the power radiated per unit area of the hole in a cavity radiator per unit wavelength. According to this definition, is the power per unit area that is emitted in the wavelength interval from to The intensity distribution among wavelengths of radiation emitted by cavities was studied experimentally at the end of the nineteenth century. Generally, radiation emitted by materials only approximately follows the blackbody radiation curve ( [link] ); however, spectra of common stars do follow the blackbody radiation curve very closely.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?