| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Light diffracts as it moves through space, bending around obstacles, interfering constructively and destructively. This can be used as a spectroscopic tool—a diffraction grating disperses light according to wavelength, for example, and is used to produce spectra—but diffraction also limits the detail we can obtain in images.
[link] (a) shows the effect of passing light through a small circular aperture . Instead of a bright spot with sharp edges, we obtain a spot with a fuzzy edge surrounded by circles of light. This pattern is caused by diffraction, similar to that produced by a single slit. Light from different parts of the circular aperture interferes constructively and destructively. The effect is most noticeable when the aperture is small, but the effect is there for large apertures as well.
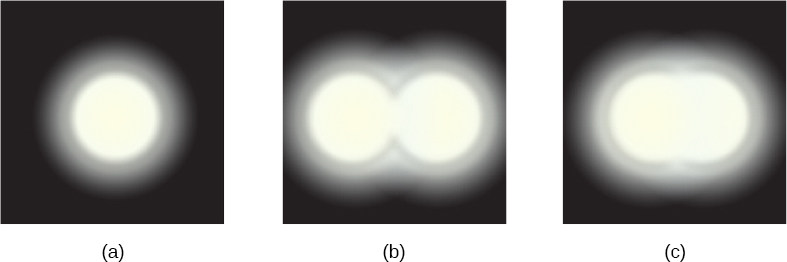
How does diffraction affect the detail that can be observed when light passes through an aperture? [link] (b) shows the diffraction pattern produced by two point-light sources that are close to one another. The pattern is similar to that for a single point source, and it is still possible to tell that there are two light sources rather than one. If they are closer together, as in [link] (c), we cannot distinguish them, thus limiting the detail or resolution we can obtain. This limit is an inescapable consequence of the wave nature of light.
Diffraction limits the resolution in many situations. The acuity of our vision is limited because light passes through the pupil, which is the circular aperture of the eye. Be aware that the diffraction-like spreading of light is due to the limited diameter of a light beam, not the interaction with an aperture. Thus, light passing through a lens with a diameter D shows this effect and spreads, blurring the image, just as light passing through an aperture of diameter D does. Thus, diffraction limits the resolution of any system having a lens or mirror. Telescopes are also limited by diffraction, because of the finite diameter D of the primary mirror.
Just what is the limit? To answer that question, consider the diffraction pattern for a circular aperture, which has a central maximum that is wider and brighter than the maxima surrounding it (similar to a slit) ( [link] (a)). It can be shown that, for a circular aperture of diameter D , the first minimum in the diffraction pattern occurs at (providing the aperture is large compared with the wavelength of light, which is the case for most optical instruments). The accepted criterion for determining the diffraction limit to resolution based on this angle is known as the Rayleigh criterion , which was developed by Lord Rayleigh in the nineteenth century.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?