| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Microscopes and telescopes are major instruments that have contributed hugely to our current understanding of the micro- and macroscopic worlds. The invention of these devices led to numerous discoveries in disciplines such as physics, astronomy, and biology, to name a few. In this section, we explain the basic physics that make these instruments work.
Although the eye is marvelous in its ability to see objects large and small, it obviously is limited in the smallest details it can detect. The desire to see beyond what is possible with the naked eye led to the use of optical instruments. We have seen that a simple convex lens can create a magnified image, but it is hard to get large magnification with such a lens. A magnification greater than is difficult without distorting the image. To get higher magnification, we can combine the simple magnifying glass with one or more additional lenses. In this section, we examine microscopes that enlarge the details that we cannot see with the naked eye.
Microscopes were first developed in the early 1600s by eyeglass makers in The Netherlands and Denmark. The simplest compound microscope is constructed from two convex lenses ( [link] ). The objective lens is a convex lens of short focal length (i.e., high power) with typical magnification from to . The eyepiece , also referred to as the ocular, is a convex lens of longer focal length.
The purpose of a microscope is to create magnified images of small objects, and both lenses contribute to the final magnification. Also, the final enlarged image is produced sufficiently far from the observer to be easily viewed, since the eye cannot focus on objects or images that are too close (i.e., closer than the near point of the eye).
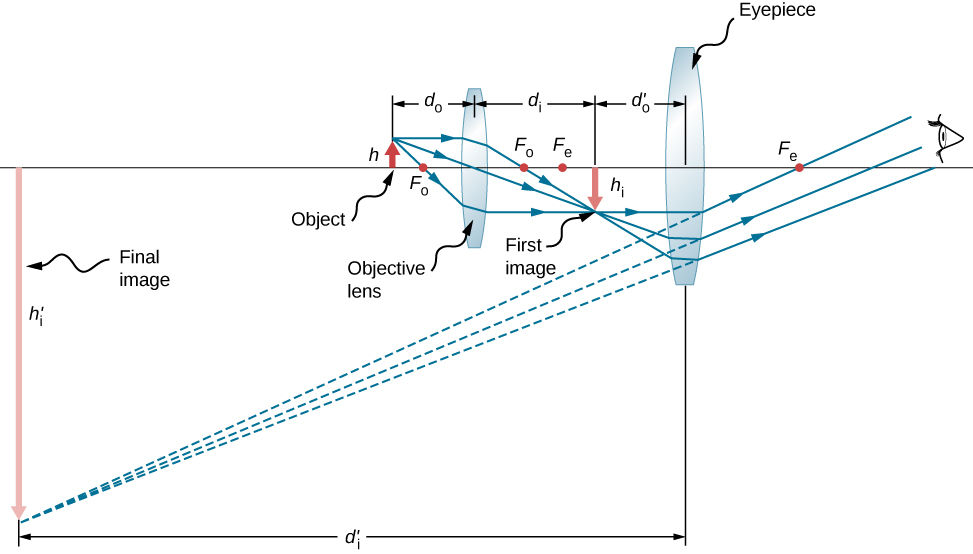
To see how the microscope in [link] forms an image, consider its two lenses in succession. The object is just beyond the focal length of the objective lens, producing a real, inverted image that is larger than the object. This first image serves as the object for the second lens, or eyepiece. The eyepiece is positioned so that the first image is within its focal length , so that it can further magnify the image. In a sense, it acts as a magnifying glass that magnifies the intermediate image produced by the objective. The image produced by the eyepiece is a magnified virtual image. The final image remains inverted but is farther from the observer than the object, making it easy to view.
The eye views the virtual image created by the eyepiece, which serves as the object for the lens in the eye. The virtual image formed by the eyepiece is well outside the focal length of the eye, so the eye forms a real image on the retina.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?