| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Lenses are found in a huge array of optical instruments, ranging from a simple magnifying glass to a camera’s zoom lens to the eye itself. In this section, we use the Snell’s law to explore the properties of lenses and how they form images.
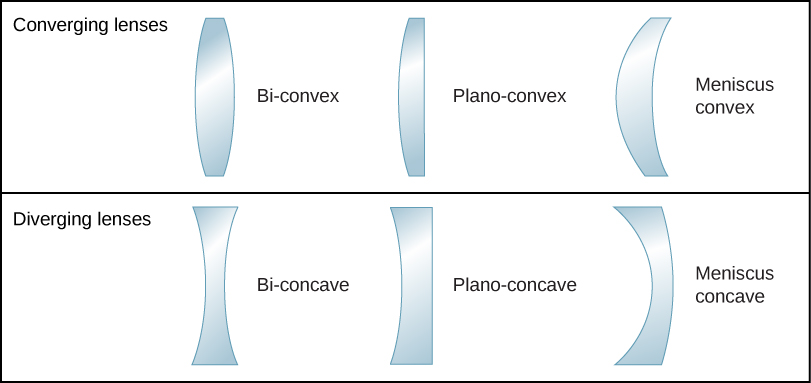
The word “lens” derives from the Latin word for a lentil bean, the shape of which is similar to a convex lens. However, not all lenses have the same shape. [link] shows a variety of different lens shapes. The vocabulary used to describe lenses is the same as that used for spherical mirrors: The axis of symmetry of a lens is called the optical axis, where this axis intersects the lens surface is called the vertex of the lens, and so forth.
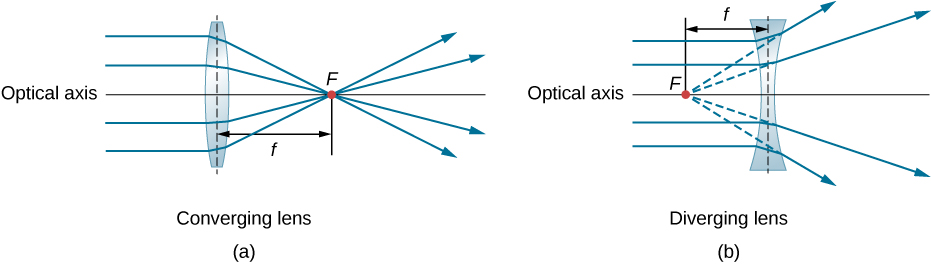
A convex or converging lens is shaped so that all light rays that enter it parallel to its optical axis intersect (or focus) at a single point on the optical axis on the opposite side of the lens, as shown in part (a) of [link] . Likewise, a concave or diverging lens is shaped so that all rays that enter it parallel to its optical axis diverge, as shown in part (b). To understand more precisely how a lens manipulates light, look closely at the top ray that goes through the converging lens in part (a). Because the index of refraction of the lens is greater than that of air, Snell’s law tells us that the ray is bent toward the perpendicular to the interface as it enters the lens. Likewise, when the ray exits the lens, it is bent away from the perpendicular. The same reasoning applies to the diverging lenses, as shown in part (b). The overall effect is that light rays are bent toward the optical axis for a converging lens and away from the optical axis for diverging lenses. For a converging lens, the point at which the rays cross is the focal point F of the lens. For a diverging lens, the point from which the rays appear to originate is the (virtual) focal point. The distance from the center of the lens to its focal point is the focal length f of the lens.
A lens is considered to be thin if its thickness t is much less than the radii of curvature of both surfaces, as shown in [link] . In this case, the rays may be considered to bend once at the center of the lens. For the case drawn in the figure, light ray 1 is parallel to the optical axis, so the outgoing ray is bent once at the center of the lens and goes through the focal point. Another important characteristic of thin lenses is that light rays that pass through the center of the lens are undeviated, as shown by light ray 2.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?