| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In 1896, Antoine Becquerel discovered that a uranium-rich rock emits invisible rays that can darken a photographic plate in an enclosed container. Scientists offer three arguments for the nuclear origin of these rays. First, the effects of the radiation do not vary with chemical state; that is, whether the emitting material is in the form of an element or compound. Second, the radiation does not vary with changes in temperature or pressure—both factors that in sufficient degree can affect electrons in an atom. Third, the very large energy of the invisible rays (up to hundreds of eV) is not consistent with atomic electron transitions (only a few eV). Today, this radiation is explained by the conversion of mass into energy deep within the nucleus of an atom. The spontaneous emission of radiation from nuclei is called nuclear radioactivity ( [link] ).

When an individual nucleus transforms into another with the emission of radiation, the nucleus is said to decay . Radioactive decay occurs for all nuclei with and also for some unstable isotopes with The decay rate is proportional to the number of original (undecayed) nuclei N in a substance. The number of nuclei lost to decay, in time interval dt , is written
where is called the decay constant . (The minus sign indicates the number of original nuclei decreases over time.) In other words, the more nuclei available to decay, the more that do decay (in time dt ). This equation can be rewritten as
Integrating both sides of the equation, and defining to be the number of nuclei at , we obtain
This gives us
Taking the left and right sides of the equation as a power of e , we have the radioactive decay law .
The total number N of radioactive nuclei remaining after time t is
where is the decay constant for the particular nucleus.
The total number of nuclei drops very rapidly at first, and then more slowly ( [link] ).
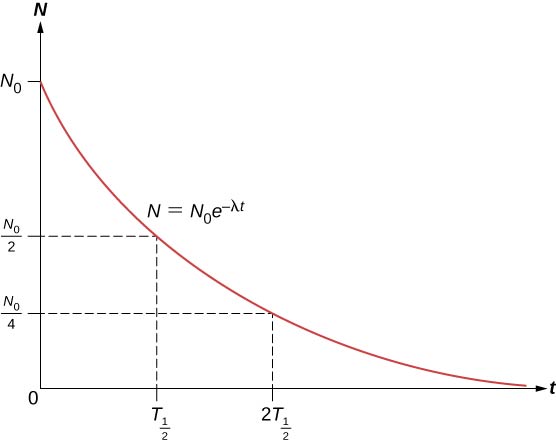
The half-life of a radioactive substance is defined as the time for half of the original nuclei to decay (or the time at which half of the original nuclei remain). The half-lives of unstable isotopes are shown in the chart of nuclides in [link] . The number of radioactive nuclei remaining after an integer ( n ) number of half-lives is therefore
If the decay constant ( ) is large, the half-life is small, and vice versa. To determine the relationship between these quantities, note that when , then . Thus, [link] can be rewritten as

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?