| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The cycles we used to describe the engine in the preceding section are all reversible, so each sequence of steps can just as easily be performed in the opposite direction. In this case, the engine is known as a refrigerator or a heat pump, depending on what is the focus: the heat removed from the cold reservoir or the heat dumped to the hot reservoir. Either a refrigerator or a heat pump is an engine running in reverse. For a refrigerator , the focus is on removing heat from a specific area. For a heat pump , the focus is on dumping heat to a specific area.
We first consider a refrigerator ( [link] ). The purpose of this engine is to remove heat from the cold reservoir, which is the space inside the refrigerator for an actual household refrigerator or the space inside a building for an air-conditioning unit.
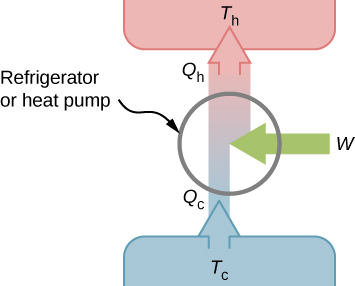
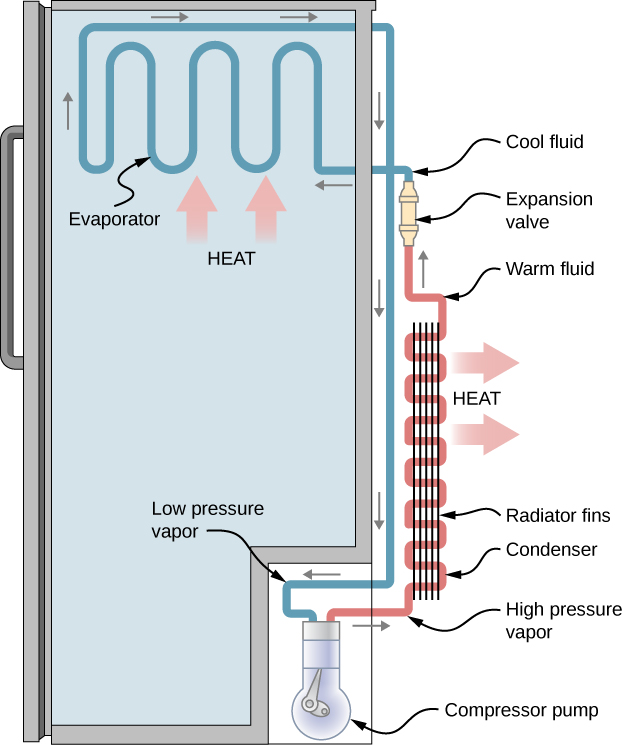
A refrigerator (or heat pump) absorbs heat from the cold reservoir at Kelvin temperature and discards heat to the hot reservoir at Kelvin temperature while work W is done on the engine’s working substance, as shown by the arrow pointing toward the system in the figure. A household refrigerator removes heat from the food within it while exhausting heat to the surrounding air. The required work, for which we pay in our electricity bill, is performed by the motor that moves a coolant through the coils. A schematic sketch of a household refrigerator is given in [link] .
The effectiveness or coefficient of performance of a refrigerator is measured by the heat removed from the cold reservoir divided by the work done by the working substance cycle by cycle:
Note that we have used the condition of energy conservation, in the final step of this expression.
The effectiveness or coefficient of performance of a heat pump is measured by the heat dumped to the hot reservoir divided by the work done to the engine on the working substance cycle by cycle:
Once again, we use the energy conservation condition to obtain the final step of this expression.
If the refrigerator door is left open, what happens to the temperature of the kitchen?
The temperature increases since the heat output behind the refrigerator is greater than the cooling from the inside of the refrigerator.
Is it possible for the efficiency of a reversible engine to be greater than 1.0? Is it possible for the coefficient of performance of a reversible refrigerator to be less than 1.0?
A refrigerator has a coefficient of performance of 3.0. (a) If it requires 200 J of work per cycle, how much heat per cycle does it remove the cold reservoir? (b) How much heat per cycle is discarded to the hot reservoir?
a. 600 J; b. 800 J
During one cycle, a refrigerator removes 500 J from a cold reservoir and rejects 800 J to its hot reservoir. (a) What is its coefficient of performance? (b) How much work per cycle does it require to operate?
If a refrigerator discards 80 J of heat per cycle and its coefficient of performance is 6.0, what are (a) the quantity off heat it removes per cycle from a cold reservoir and (b) the amount of work per cycle required for its operation?
a. 69 J; b. 11 J
A refrigerator has a coefficient of performance of 3.0. (a) If it requires 200 J of work per cycle, how much heat per cycle does it remove the cold reservoir? (b) How much heat per cycle is discarded to the hot reservoir?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?