| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Consider an ideal gas that is held in half of a thermally insulated container by a wall in the middle of the container. The other half of the container is under vacuum with no molecules inside. Now, if we remove the wall in the middle quickly, the gas expands and fills up the entire container immediately, as shown in [link] .
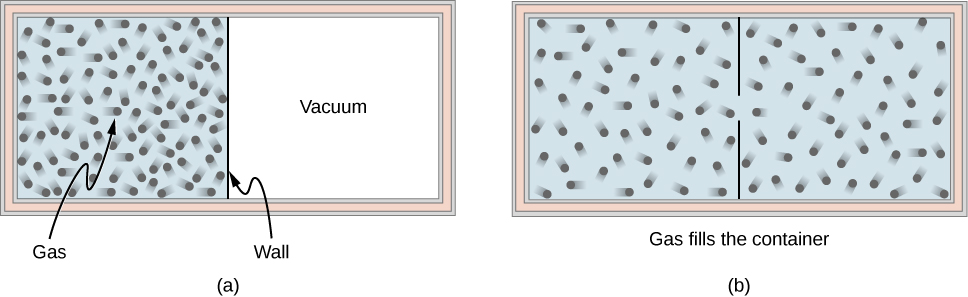
Because half of the container is under vacuum before the gas expands there, we do not expect any work to be done by the system—that is, —because no force from the vacuum is exerted on the gas during the expansion. If the container is thermally insulated from the rest of the environment, we do not expect any heat transfer to the system either, so . Then the first law of thermodynamics leads to the change of the internal energy of the system,
For an ideal gas, if the internal energy doesn’t change, then the temperature stays the same. Thus, the equation of state of the ideal gas gives us the final pressure of the gas, where is the pressure of the gas before the expansion. The volume is doubled and the pressure is halved, but nothing else seems to have changed during the expansion.
All of this discussion is based on what we have learned so far and makes sense. Here is what puzzles us: Can all the molecules go backward to the original half of the container in some future time? Our intuition tells us that this is going to be very unlikely, even though nothing we have learned so far prevents such an event from happening, regardless of how small the probability is. What we are really asking is whether the expansion into the vacuum half of the container is reversible .
A reversible process is a process in which the system and environment can be restored to exactly the same initial states that they were in before the process occurred, if we go backward along the path of the process. The necessary condition for a reversible process is therefore the quasi-static requirement. Note that it is quite easy to restore a system to its original state; the hard part is to have its environment restored to its original state at the same time. For example, in the example of an ideal gas expanding into vacuum to twice its original volume, we can easily push it back with a piston and restore its temperature and pressure by removing some heat from the gas. The problem is that we cannot do it without changing something in its surroundings, such as dumping some heat there.
A reversible process is truly an ideal process that rarely happens. We can make certain processes close to reversible and therefore use the consequences of the corresponding reversible processes as a starting point or reference. In reality, almost all processes are irreversible, and some properties of the environment are altered when the properties of the system are restored. The expansion of an ideal gas, as we have just outlined, is irreversible because the process is not even quasi-static, that is, not in an equilibrium state at any moment of the expansion.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?