| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Particles in an ideal gas all travel at relatively high speeds, but they do not travel at the same speed. The rms speed is one kind of average, but many particles move faster and many move slower. The actual distribution of speeds has several interesting implications for other areas of physics, as we will see in later chapters.
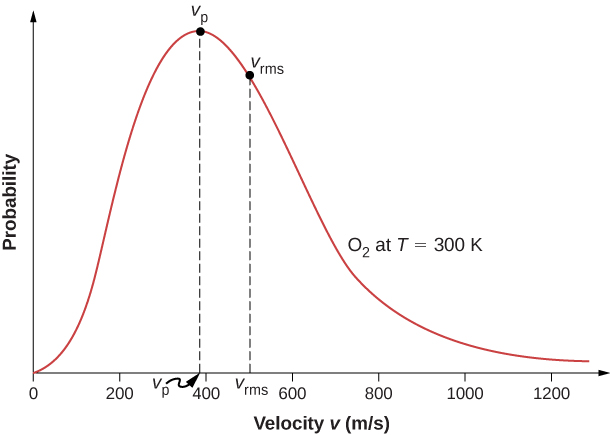
The motion of molecules in a gas is random in magnitude and direction for individual molecules, but a gas of many molecules has a predictable distribution of molecular speeds. This predictable distribution of molecular speeds is known as the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution , after its originators, who calculated it based on kinetic theory, and it has since been confirmed experimentally ( [link] ).
To understand this figure, we must define a distribution function of molecular speeds, since with a finite number of molecules, the probability that a molecule will have exactly a given speed is 0.
We define the distribution function by saying that the expected number of particles with speeds between and is given by
[Since N is dimensionless, the unit of f ( v ) is seconds per meter.] We can write this equation conveniently in differential form:
In this form, we can understand the equation as saying that the number of molecules with speeds between v and is the total number of molecules in the sample times f ( v ) times dv . That is, the probability that a molecule’s speed is between v and is f ( v ) dv .
We can now quote Maxwell’s result, although the proof is beyond our scope.
The distribution function for speeds of particles in an ideal gas at temperature T is
The factors before the are a normalization constant; they make sure that by making sure that Let’s focus on the dependence on v . The factor of means that and for small v , the curve looks like a parabola. The factor of means that and the graph has an exponential tail, which indicates that a few molecules may move at several times the rms speed. The interaction of these factors gives the function the single-peaked shape shown in the figure.
All we have to do is take the ratio of the two f values.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?