| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The ac circuit shown in [link] , called an RLC series circuit , is a series combination of a resistor, capacitor, and inductor connected across an ac source. It produces an emf of
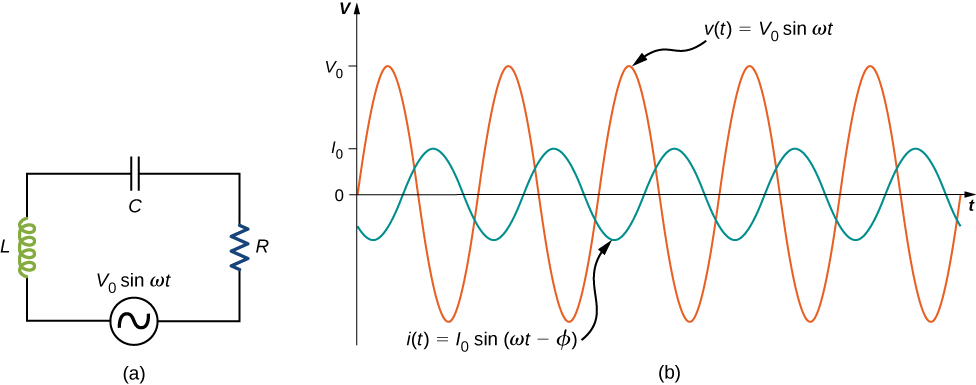
Since the elements are in series, the same current flows through each element at all points in time. The relative phase between the current and the emf is not obvious when all three elements are present. Consequently, we represent the current by the general expression
where is the current amplitude and is the phase angle between the current and the applied voltage. The phase angle is thus the amount by which the voltage and current are out of phase with each other in a circuit. Our task is to find
A phasor diagram involving is helpful for analyzing the circuit. As shown in [link] , the phasor representing points in the same direction as the phasor for its amplitude is The phasor lags the i ( t ) phasor by rad and has the amplitude The phasor for leads the i ( t ) phasor by rad and has the amplitude
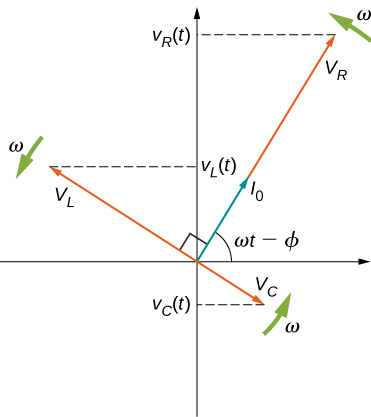
At any instant, the voltage across the RLC combination is the emf of the source. Since a component of a sum of vectors is the sum of the components of the individual vectors—for example, —the projection of the vector sum of phasors onto the vertical axis is the sum of the vertical projections of the individual phasors. Hence, if we add vectorially the phasors representing and then find the projection of the resultant onto the vertical axis, we obtain
The vector sum of the phasors is shown in [link] . The resultant phasor has an amplitude and is directed at an angle with respect to the or i ( t ), phasor. The projection of this resultant phasor onto the vertical axis is We can easily determine the unknown quantities and from the geometry of the phasor diagram. For the phase angle,
and after cancellation of this becomes
Furthermore, from the Pythagorean theorem,
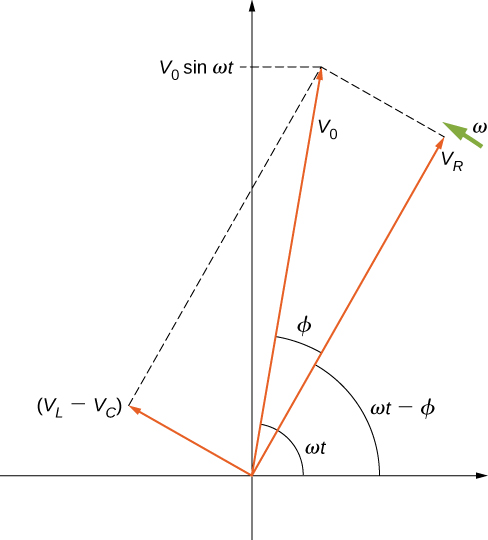
The current amplitude is therefore the ac version of Ohm’s law:
where
is known as the impedance of the circuit. Its unit is the ohm, and it is the ac analog to resistance in a dc circuit, which measures the combined effect of resistance, capacitive reactance, and inductive reactance ( [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?