| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
When you use a flash camera, it takes a few seconds to charge the capacitor that powers the flash. The light flash discharges the capacitor in a tiny fraction of a second. Why does charging take longer than discharging? This question and several other phenomena that involve charging and discharging capacitors are discussed in this module.
An RC circuit is a circuit containing resistance and capacitance. As presented in Capacitance , the capacitor is an electrical component that stores electric charge, storing energy in an electric field.
[link] (a) shows a simple RC circuit that employs a dc (direct current) voltage source , a resistor R , a capacitor C , and a two-position switch. The circuit allows the capacitor to be charged or discharged, depending on the position of the switch. When the switch is moved to position A , the capacitor charges, resulting in the circuit in part (b). When the switch is moved to position B , the capacitor discharges through the resistor.
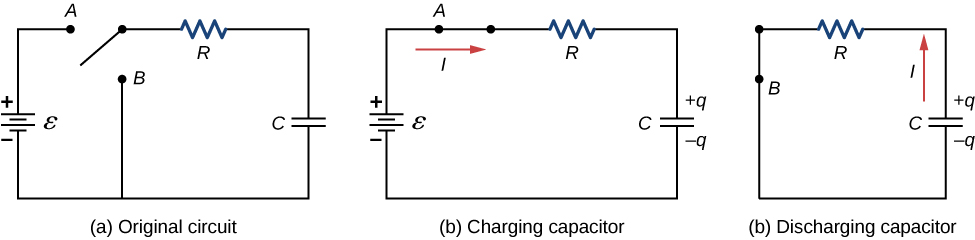
We can use Kirchhoff’s loop rule to understand the charging of the capacitor. This results in the equation This equation can be used to model the charge as a function of time as the capacitor charges. Capacitance is defined as so the voltage across the capacitor is . Using Ohm’s law, the potential drop across the resistor is , and the current is defined as
This differential equation can be integrated to find an equation for the charge on the capacitor as a function of time.
Let , then The result is
Simplifying results in an equation for the charge on the charging capacitor as a function of time:
A graph of the charge on the capacitor versus time is shown in [link] (a). First note that as time approaches infinity, the exponential goes to zero, so the charge approaches the maximum charge and has units of coulombs. The units of RC are seconds, units of time. This quantity is known as the time constant :
At time , the charge is equal to of the maximum charge . Notice that the time rate change of the charge is the slope at a point of the charge versus time plot. The slope of the graph is large at time and approaches zero as time increases.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?