| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
We have seen in previous chapters that energy is one of the fundamental concepts of physics. Heat is a type of energy transfer that is caused by a temperature difference, and it can change the temperature of an object. As we learned earlier in this chapter, heat transfer is the movement of energy from one place or material to another as a result of a difference in temperature. Heat transfer is fundamental to such everyday activities as home heating and cooking, as well as many industrial processes. It also forms a basis for the topics in the remainder of this chapter.
We also introduce the concept of internal energy, which can be increased or decreased by heat transfer. We discuss another way to change the internal energy of a system, namely doing work on it. Thus, we are beginning the study of the relationship of heat and work, which is the basis of engines and refrigerators and the central topic (and origin of the name) of thermodynamics.
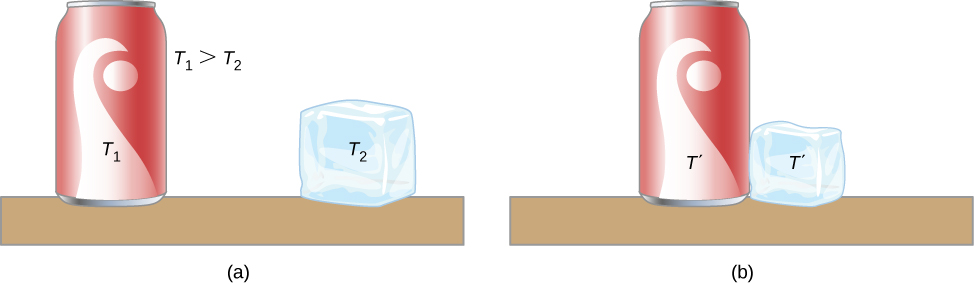
A thermal system has internal energy (also called thermal energy ) , which is the sum of the mechanical energies of its molecules. A system’s internal energy is proportional to its temperature. As we saw earlier in this chapter, if two objects at different temperatures are brought into contact with each other, energy is transferred from the hotter to the colder object until the bodies reach thermal equilibrium (that is, they are at the same temperature). No work is done by either object because no force acts through a distance (as we discussed in Work and Kinetic Energy ). These observations reveal that heat is energy transferred spontaneously due to a temperature difference. [link] shows an example of heat transfer.
The meaning of “heat” in physics is different from its ordinary meaning. For example, in conversation, we may say “the heat was unbearable,” but in physics, we would say that the temperature was high. Heat is a form of energy flow, whereas temperature is not. Incidentally, humans are sensitive to heat flow rather than to temperature.
Since heat is a form of energy, its SI unit is the joule (J). Another common unit of energy often used for heat is the calorie (cal), defined as the energy needed to change the temperature of 1.00 g of water by —specifically, between and , since there is a slight temperature dependence. Also commonly used is the kilocalorie (kcal), which is the energy needed to change the temperature of 1.00 kg of water by . Since mass is most often specified in kilograms, the kilocalorie is convenient. Confusingly, food calories (sometimes called “big calories,” abbreviated Cal) are actually kilocalories, a fact not easily determined from package labeling.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'University physics volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?