| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
An alcohol is any organic compound where there is a hydroxyl functional group (-OH) bound to a carbon atom. The general formula for a simple alcohol is C H OH.
The simplest and most commonly used alcohols are methanol and ethanol ( [link] ).
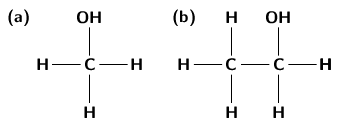
The alcohols have a number of different uses:
Fermentation' refers to the conversion of sugar to alcohol using yeast (a fungus). The process of fermentation produces items such as wine, beer and yoghurt. To make wine, grape juice is fermented to produce alcohol. This reaction is shown below:
Ethanol is a diuretic. In humans, ethanol reduces the secretion of a hormone called antidiuretic hormone (ADH). The role of ADH is to control the amount of water that the body retains. When this hormone is not secreted in the right quantities, it can cause dehyration because too much water is lost from the body in the urine. This is why people who drink too much alcohol can become dehydrated, and experience symptoms such as headaches, dry mouth, and lethargy. Part of the reason for the headaches is that dehydration causes the brain to shrink away from the skull slightly. The effects of drinking too much alcohol can be reduced by drinking lots of water.
The rules used to name the alcohols are similar to those already discussed for the other compounds, except that the suffix of the name will be different because the compound is an alcohol.
Khan academy video on alcohols
Give the IUPAC name for the following organic compound
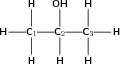
The compound has an -OH (hydroxyl) functional group and is therefore an alcohol. The compound will have the suffix -ol.
There are three carbons in the longest chain. The prefix for this compound will be 'prop'. Since there are only single bonds between the carbon atoms, the suffix becomes 'propan' (similar to the alkane 'propane').
In this case, it doesn't matter whether you start numbering from the left or right. The hydroxyl group will still be attached to the middle carbon atom, numbered '2'.
There are no branched groups in this compound, but you still need to indicate the position of the hydroxyl group on the second carbon. The suffix will be -2-ol because the hydroxyl group is attached to the second carbon.
The compound's name is propan-2-ol.
Give the IUPAC name for the following compound:
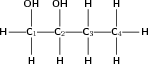
The compound has an -OH (hydroxyl) functional group and is therefore an alcohol. There are two hydroxyl groups in the compound, so the suffix will be -diol.
There are four carbons in the longest chain. The prefix for this compound will be 'butan'.
The carbons will be numbered from left to right so that the two hydroxyl groups are attached to carbon atoms with the lowest numbers.
There are no branched groups in this compound, but you still need to indicate the position of the hydroxyl groups on the first and second carbon atoms. The suffix will therefore become 1,2-diol.
The compound's name is butan-1,2-diol.
The hydroxyl group affects the solubility of the alcohols. The hydroxyl group generally makes the alcohol molecule polar and therefore more likely to be soluble in water. However, the carbon chain resists solubility, so there are two opposing trends in the alcohols. Alcohols with shorter carbon chains are usually more soluble than those with longer carbon chains.
Alcohols tend to have higher boiling points than the hydrocarbons because of the strong hydrogen bond between hydrogen and oxygen atoms.
Alcohols can show either acidic or basic properties because of the hydroxyl group. They also undergo oxidation reactions to form aldehydes, ketones and carboxylic acids.
Read the extract below and then answer the questions that follow:
The alcohols are a very important group of organic compounds, and they have a variety of uses. Our most common use of the word 'alcohol' is with reference to alcoholic drinks. The alcohol in drinks is in fact ethanol . But ethanol has many more uses apart from alcoholic drinks! When ethanol burns in air, it produces carbon dioxide, water and energy and can therefore be used as a fuel on its own, or in mixtures with petrol. Because ethanol can be produced through fermentation, this is a useful way for countries without an oil industry to reduce imports of petrol. Ethanol is also used as a solvent in many perfumes and cosmetics.
Methanol can also be used as a fuel, or as a petrol additive to improve combustion. Most methanol is used as an industrial feedstock, in other words it is used to make other things such as methanal (formaldehyde), ethanoic acid and methyl esters. In most cases, these are then turned into other products.
Propan-2-ol is another important alcohol, which is used in a variety of applications as a solvent.
Questions

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula textbooks: grade 12 physical science' conversation and receive update notifications?