| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In Grade 11 you learnt how a magnetic field is generated around a current carrying conductor. You also learnt how a current is generated in a conductor that moves in a magnetic field. This chapter describes how conductors moving in a magnetic field are applied in the real-world.
We have seen that when a conductor is moved in a magnetic field or when a magnet is moved near a conductor, a current flows in the conductor. The amount of current depends on the speed at which the conductor experiences a changing magnetic field, the number of turns of the conductor and the position of the plane of the conductor with respect to the magnetic field. The effect of the orientation of the conductor with respect to the magnetic field is illustrated in [link] .
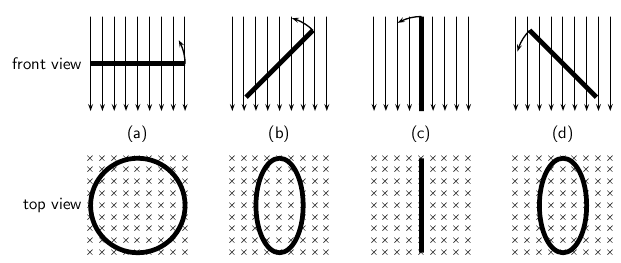
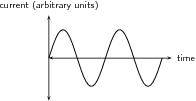
If the current flowing in the conductor were plotted as a function of the angle between the plane of the conductor and the magnetic field, then the current would vary as shown in [link] . The current alternates about zero and is known as an alternating current (abbreviated AC).
Recall Faraday's Law which you learnt about in Grade 11:
The emf (electromotive force), , produced around a loop of conductor is proportional to the rate of change of the magnetic flux, , through the area, , of the loop. This can be stated mathematically as:
where and is the strength of the magnetic field.
Faraday's Law relates induced emf (electromotive force) to the rate of change of flux, which is the product of the magnetic field and the cross-sectionalarea the field lines pass through. As the closed loop conductor changes orientation with respect to the magnetic field, the amount of magnetic flux through the area of the loop changes, and an emf is induced in the conducting loop.
The principle of rotating a conductor in a magnetic field is used in electrictrical generators. A generator converts mechanical energy (motion) into electrical energy.
A generator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
The layout of a simple AC generator is shown in [link] . The conductor in the shape of a coil is connected to a slip ring. The conductor is then manually rotated in the magnetic field generating an alternating emf. The slip rings are connected to the load via brushes.

If a machine is constructed to rotate a magnetic field around a set of stationary wire coils with the turning of a shaft, AC voltage will be produced across the wire coils as that shaft is rotated, in accordance with Faraday's Law of electromagnetic induction. This is the basic operating principle of an AC generator.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula textbooks: grade 12 physical science' conversation and receive update notifications?