| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In this chapter we will look at some mechanical (physical) properties of various materials that we use. The mechanical properties of a material are those properties that are affected by forces being applied to the material. These properties are important to consider when we are constructing buildings, structures or modes of transport like an aeroplane.
Deformation (change of shape) of a solid is caused by a force that can either be compressive or tensile when applied in one direction (plane). Compressive forces try to compress the object (make it smaller or more compact) while tensile forces try to tear it apart. We can study these effects by looking at what happens when you compress or expand a spring.
Hooke's Law relates the restoring force of a spring to its displacement from equilibrium length.
The equilibrium length of a spring is its length when no forces are applied to it. When a force is applied to a spring, e.g., by attaching a weight to one end, the spring will expand and become longer. The difference between the new length and the equilibrium length is the displacement.
In an elastic spring, the extension varies linearly with the force applied.
where is the restoring force in newtons (N), is the spring constant in and is the displacement of the spring from its equilibrium length in metres (m).
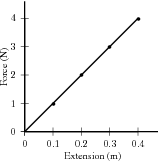
Aim:
Verify Hooke's Law.
Apparatus:
Method:
Conclusions:
Phet simulation for hooke's law
Khan academy video on springs and hooke's law
A spring is extended by 7 cm by a force of 56 N.
Calculate the spring constant for this spring.
A spring of length 20cm stretches to 24cm when a load of 0,6N is applied to it.
We know:
= 0,6 N
The equilibrium spring length is 20 cm
The expanded spring length is 24 cm
First we need to calculate the displacement of the spring from its equilibrium length:
Now use Hooke's Law to find the spring constant:
= 0,5 N
We know from the first part of the question that
= -15
So, using Hooke's Law:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula textbooks: grade 12 physical science' conversation and receive update notifications?