| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Having looked at factors that affect the rate of a reaction, we now need to ask some important questions. Does a reaction always proceed in the same direction or can it be reversible? In other words, is it always true that a reaction proceeds from reactants to products , or is it possible that sometimes, the reaction will reverse and the products will be changed back into the reactants ? And does a reaction always run its full course so that all the reactants are used up, or can a reaction reach a point where reactants are still present, but there does not seem to be any further change taking place in the reaction? The following demonstration might help to explain this.
Apparatus and materials:
2 beakers; water; bell jar
Method:
Observations:
You should notice that in the beaker that is uncovered, the water level drops quickly because of evaporation. In the beaker that is covered, there is an initial drop in the water level, but after a while evaporation appears to stop and the water level in this beaker is higher than that in the one that is open. Note that the diagram below shows the situation ate time=0.
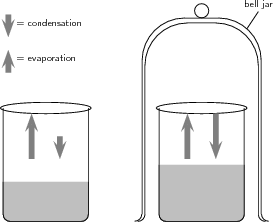
Discussion:
In the first beaker, liquid water becomes water vapour as a result of evaporation and the water level drops. In the second beaker, evaporation also takes place. However, in this case, the vapour comes into contact with the surface of the bell jar and it cools and condenses to form liquid water again. This water is returned to the beaker. Once condensation has begun, the rate at which water is lost from the beaker will start to decrease. At some point, the rate of evaporation will be equal to the rate of condensation above the beaker, and there will be no change in the water level in the beaker. This can be represented as follows:
In this example, the reaction (in this case, a change in the phase of water) can proceed in either direction. In one direction there is a change in phase from liquid to vapour. But the reverse can also take place, when vapour condenses to form water again.
In a closed system it is possible for reactions to be reversible, such as in the demonstration above. In a closed system, it is also possible for a chemical reaction to reach equilibrium . We will discuss these concepts in more detail.
An open system is one in which matter or energy can flow into or out of the system. In the liquid-vapour demonstration we used, the first beaker was an example of an open system because the beaker could be heated or cooled (a change in energy ), and water vapour (the matter ) could evaporate from the beaker.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula textbooks: grade 12 physical science' conversation and receive update notifications?