| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
It should be clear now that the rate of a reaction varies depending on a number of factors. But how can we explain why reactions take place at different speeds under different conditions? Why, for example, does an increase in the surface area of the reactants also increase the rate of the reaction? One way to explain this is to use collision theory.
For a reaction to occur, the particles that are reacting must collide with one another. Only a fraction of all the collisions that take place actually cause a chemical change. These are called 'successful' collisions. When there is an increase in the concentration of reactants, the chance that reactant particles will collide with each other also increases because there are more particles in that space. In other words, the collision frequency of the reactants increases. The number of successful collisions will therefore also increase, and so will the rate of the reaction. In the same way, if the surface area of the reactants increases, there is also a greater chance that successful collisions will occur.
Collision theory is a theory that explains how chemical reactions occur and why reaction rates differ for different reactions. The theory states that for a reaction to occur the reactant particles must collide, but that only a certain fraction of the total collisions, the effective collisions , actually cause the reactant molecules to change into products. This is because only a small number of the molecules have enough energy and the right orientation at the moment of impact to break the existing bonds and form new bonds.
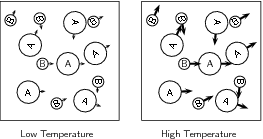
When the temperature of the reaction increases, the average kinetic energy of the reactant particles increases and they will move around much more actively. They are therefore more likely to collide with one another ( [link] ). Increasing the temperature also increases the number of particles whose energy will be greater than the activation energy for the reaction (refer "Mechanism of reaction and catalysis" ).
Hydrochloric acid and calcium carbonate react according to the following equation:
The volume of carbon dioxide that is produced during the reaction is measured at different times. The results are shown in the table below.
| Time (mins) | Total Volume of CO produced (cm ) |
| 1 | 14 |
| 2 | 26 |
| 3 | 36 |
| 4 | 44 |
| 5 | 50 |
| 6 | 58 |
| 7 | 65 |
| 8 | 70 |
| 9 | 74 |
| 10 | 77 |
Note: On a graph of production against time, it is the gradient of the graph that shows the rate of the reaction.
Questions:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula textbooks: grade 12 physical science' conversation and receive update notifications?