| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
One of the most interesting, and also very useful, properties of waves is diffraction .
Diffraction is the ability of a wave to spread out in wavefronts as the wave passes through a small aperture or around a sharp edge.
Diffraction refers to various phenomena associated with wave propagation, such as the bending, spreading and interference of waves emerging from an aperture. It occurs with any type of wave, including sound waves, water waves, electromagnetic waves such as light and radio waves. While diffraction always occurs, its effects are generally only noticeable for waves where the wavelength is on the order of the feature size of the diffracting objects or apertures.
For example, if two rooms are connected by an open doorway and a sound is produced in a remote corner of one of them, a person in the other room will hear the sound as if it originated at the doorway.
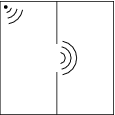
As far as the second room is concerned, the vibrating air in the doorway is the source of the sound. The same is true of light passing the edge of an obstacle, but this is not as easily observed because of the short wavelength of visible light.
This means that when waves move through small holes they appear to bend around the sides because there are not enough points on the wavefront to form another straight wavefront. This is bending round the sides we call diffraction .
Diffraction effects are more clear for water waves with longer wavelengths. Diffraction can be demonstrated by placing small barriers and obstacles in a ripple tank and observing the path of the water waves as they encounter the obstacles. The waves are seen to pass around the barrier into the regions behind it; subsequently the water behind the barrier is disturbed. The amount of diffraction (the sharpness of the bending) increases with increasing wavelength and decreases with decreasing wavelength. In fact, when the wavelength of the waves are smaller than the obstacle, no noticeable diffraction occurs.
Water waves in a ripple tank can be used to demonstrate diffraction and interference.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula textbooks: grade 12 physical science' conversation and receive update notifications?