| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
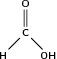
Carboxylic acids are organic acids that are characterised by having a carboxyl group, which has the formula -(C=O)-OH, or more commonly written as -COOH. In a carboxyl group, an oxygen atom is double-bonded to a carbon atom, which is also bonded to a hydroxyl group. The simplest carboxylic acid, methanoic acid, is shown in [link] . The IUPAC suffix for carboxylic acids is -anoic acid.
Carboxylic acids are widespread in nature. Methanoic acid (also known as formic acid ) has the formula HCOOH and is found in insect stings. Ethanoic acid (CH COOH), or acetic acid , is the main component of vinegar. More complex organic acids also have a variety of different functions. Benzoic acid (C H COOH) for example, is used as a food preservative.
A certain type of ant, called formicine ants, manufacture and secrete formic acid, which is used to defend themselves against other organisms that might try to eat them.
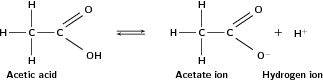
Carboxylic acids are weak acids , in other words they only dissociate partially. Why does the carboxyl group have acidic properties? In the carboxyl group, the hydrogen tends to separate itself from the oxygen atom. In other words, the carboxyl group becomes a source of positively-charged hydrogen ions (H ). This is shown in [link] .
| Formula | Common name | Source | IUPAC name | melting point ( C) | boiling point ( C) |
| formic acid | ants | methanoic acid | 8.4 | 101 | |
| CH CO H | vinegar | ethanoic acid | 16.6 | 118 | |
| propionic acid | milk | propanoic acid | -20.8 | 141 | |
| CH (CH ) CO H | butyric acid | butter | -5.5 | 164 | |
| valeric acid | valerian root | pentanoic acid | -34.5 | 186 | |
| CH (CH ) CO H | caproic acid | goats | -4 | 205 | |
| enanthic acid | vines | -7.5 | 223 | ||
| CH (CH ) CO H | caprylic acid | goats | 16.3 | 239 |
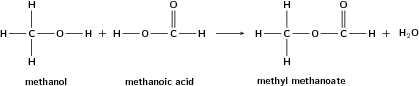
When an alcohol reacts with a carboxylic acid, an ester is formed. Most esters have a characteristic and pleasant smell. In the reaction, the hydrogen atom from the hydroxyl group, and an OH from the carboxlic acid, form a molecule of water. A new bond is formed between what remains of the alcohol and acid. The name of the ester is a combination of the names of the alcohol and carboxylic acid. The suffix for an ester is -oate. An example is shown in [link] .
The amino group has the formula -NH and consists of a nitrogen atom that is bonded to two hydrogen atoms, and to the carbon skeleton. Organic compounds that contain this functional group are called amines . One example is glycine . Glycine belongs to a group of organic compounds called amino acids , which are the building blocks of proteins.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula textbooks: grade 12 physical science' conversation and receive update notifications?