| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
If we were to cut the Earth in half we would see that our planet is made up of a number of layers, namely the core at the centre (seperated into the inner and outer core), the mantle , the upper mantle , the outer crust and the atmosphere ( [link] ). The core is made up mostly of iron. The mantle, which lies between the core and the crust, consists of molten rock, called magma which moves continuously because of convection currents. The crust is the thin, hard outer layer that 'floats' on the magma of the mantle. It is the upper part of the mantle and the crust that make up the lithosphere ('lith' means 'types of stone' and 'sphere' refers to the round shape of the earth). Together, the lithosphere, hydrosphere and atmosphere make up the world as we know it.
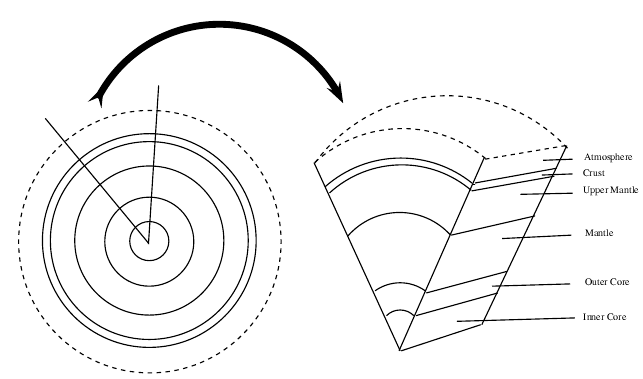
The lithosphere is the solid outermost shell of our planet. The lithosphere includes the crust and the upper part of the mantle, and is made up of material from both the continents and the oceans on the Earth's surface.
In grade 10 have focused on the hydrosphere and the atmosphere. The lithosphere is also very important, not only because it is the surface on which we live, but also because humans gain many valuable resources from this part of the planet.
The crust is made up of about 80 elements, which occur in over 2000 different compounds and minerals. However, most of the mass of the material in the crust is made up of only 8 of these elements. These are oxygen (O), silica (Si), aluminium (Al), iron (Fe), calcium (Ca), sodium (Na), potassium (K) and magnesium (Mg). These metal elements are seldom found in their pure form, but are usually part of other more complex minerals . A mineral is a compound that is formed through geological processes, which give it a particular structure. A mineral could be a pure element, but more often minerals are made up of many different elements combined. Quartz is just one example. It is a mineral that is made up of silicon and oxygen. Some more examples are shown in [link] .
Minerals are natural compounds formed through geological processes. The term 'mineral' includes both the material's chemical composition and its structure. Minerals range in composition from pure elements to complex compounds.
| Mineral | Chemistry | Comments |
| Quartz | SiO (silicon dioxide) | Quartz is used for glass, in electrical components, optical lenses and in building stone |
| Gold | Au (pure element) or AuTe (Calaverite, a gold mineral) | Gold is often found in a group of minerals called the tellurides . Calaverite is a mineral that belongs to this group, and is the most common gold-bearing mineral. Gold has an affinity for tellurium (Te). |
| Hematite | Fe O (iron oxide) | Iron usually occurs in iron oxide minerals or as an alloy of iron and nickel. |
| Orthoclase | KAlSi O (potassium aluminium silicate) | Orthoclase belongs to the feldspar group of minerals. |
| Copper | Cu (pure element) or Cu (CO )(OH) (malachite or copper carbonate hydroxide) | copper can be mined as a pure element or as a mineral such as malachite. |

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula textbooks: grade 11 physical science' conversation and receive update notifications?